Betulonic acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 08:56:59
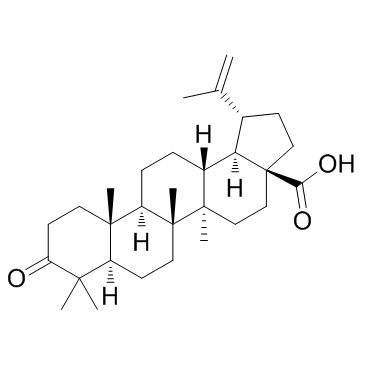
Betulonic acid structure
|
Common Name | Betulonic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4481-62-3 | Molecular Weight | 454.684 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 548.1±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H46O3 | Melting Point | 264 °C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 299.4±21.9 °C | |
Use of Betulonic acidBetulonic acid belongs to the pentacyclic triterpenic derivative class, has antitumor activities.In vitro: BEA-NP is found over three-times more permeable than that solubilized by DMSO in Caco-2 cell monocultures.[1]In vivo: The tumor growth in the S180 berry mice orally doses with BEA-NP at 75 mg/kg is inhibited by 50%. Rubusoside is effective in solubilizing BEA, maintaining its cytotoxicity, enhancing its permeability and reducing tumor growth when orally administered.[1] antitumor activities against MGC-803, PC3, Bcap-37, A375, and MCF-7 human cancer cell lines In vivo: The animals are treated with betulonic acid amide (50 mg/kg in Tween aqueous solution) and heptral (6 mg/kg) as hepatoprotective compounds. It is found that betulonic acid amide stimulats the regenerative response in hepatocytes under conditions of combined toxic exposure and promots recovery of their qualitative and quantitative characteristics. [2] |
| Name | Betulonicacid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Betulonic acid belongs to the pentacyclic triterpenic derivative class, has antitumor activities.In vitro: BEA-NP is found over three-times more permeable than that solubilized by DMSO in Caco-2 cell monocultures.[1]In vivo: The tumor growth in the S180 berry mice orally doses with BEA-NP at 75 mg/kg is inhibited by 50%. Rubusoside is effective in solubilizing BEA, maintaining its cytotoxicity, enhancing its permeability and reducing tumor growth when orally administered.[1] antitumor activities against MGC-803, PC3, Bcap-37, A375, and MCF-7 human cancer cell lines In vivo: The animals are treated with betulonic acid amide (50 mg/kg in Tween aqueous solution) and heptral (6 mg/kg) as hepatoprotective compounds. It is found that betulonic acid amide stimulats the regenerative response in hepatocytes under conditions of combined toxic exposure and promots recovery of their qualitative and quantitative characteristics. [2] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 548.1±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 264 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C30H46O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 454.684 |
| Flash Point | 299.4±21.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 454.344696 |
| PSA | 54.37000 |
| LogP | 8.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.527 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| Betulinonic acid |
| 3-Oxolup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid |
| Liquidambaricacid |
| Betulonic acid |
| Lup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid, 3-oxo- |
| LiquidaMba |
 CAS#:472-15-1
CAS#:472-15-1 CAS#:473-98-3
CAS#:473-98-3 CAS#:13159-28-9
CAS#:13159-28-9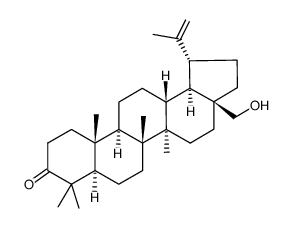 CAS#:7020-34-0
CAS#:7020-34-0 CAS#:1721-69-3
CAS#:1721-69-3![(1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aR,11bR,13bR)-3a-(hydroxymethyl)-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-1-(prop-1-en-2-yl)icosahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]chrysen-9-ol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/057/1072913-62-2.png) CAS#:1072913-62-2
CAS#:1072913-62-2 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7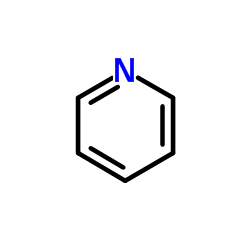 CAS#:110-86-1
CAS#:110-86-1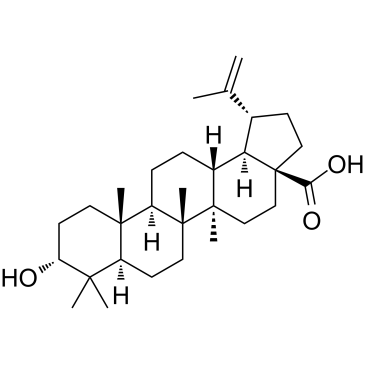 CAS#:38736-77-5
CAS#:38736-77-5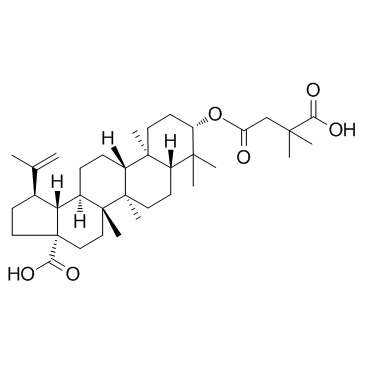 CAS#:174022-42-5
CAS#:174022-42-5![11-[[(1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-9-oxo-1-prop-1-en-2-yl-2,3,4,5,6,7,7a,10,11,11b,12,13,13a,13b-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]chrysene-3a-carbonyl]amino]undecanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/252/150840-33-8.png) CAS#:150840-33-8
CAS#:150840-33-8
