Betulinic acid
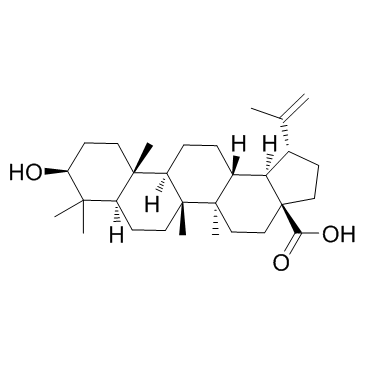
Betulinic acid structure
|
Common Name | Betulinic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 472-15-1 | Molecular Weight | 456.700 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 550.0±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 | Melting Point | 295-298 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 300.5±21.9 °C | |
Use of Betulinic acidBetulinic acid is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid, acts as a eukaryotic topoisomerase I inhibitor, with an IC50 of 5 μM, and possesses anti-HIV, anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. |
| Name | betulinic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Betulinic acid is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid, acts as a eukaryotic topoisomerase I inhibitor, with an IC50 of 5 μM, and possesses anti-HIV, anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase I:5 μM (IC50) HIV-1:1.4 μM (EC50) |
| In Vitro | Betulinic acid is a eukaryotic topoisomerase I inhibitor, with an IC50 of 5 μM, and prevents topoisomerase I-DNA interaction[1]. Betulinic acid (10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 µM) significantly suppresses MDA-MB-231 cell viability in a time- and dose-dependent manner after treatment for 24 or 48 h. Betulinic acid (20, 40 µM) causes decrease in Bcl-2 expression of MDA-MB-231 cells. Betulinic acid also induces morphological changes of MDA-MB-231 cells at 20 µM, and leads to ultrastructure changes of MDA-MB-231 cells at 40 µM[2]. Betulinic acid shows anti-HIV activities, with an EC50 of 1.4 µM in acutely infected H9 lymphocytes[4]. |
| In Vivo | Betulinic acid (10 and 30 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly abrogates colon shortening, and reduces malondialdehyde (MDA) and lipid hydroperoxide levels in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Betulinic acid (30 mg/kg, p.o.) restores superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase activity and glutathione (GSH) content to control levels in DSS-induced colitis in mice. Betulinic acid (30 mg/kg, p.o.) also inhibits the DSS-induced increase in inflammatory markers. Betulinic acid (3, 10, 30 mg/kg, p.o.) suppresses acetic acid-induced writhing responses and mustard oil (MO)-induced visceral nociception in mice[3]. |
| Cell Assay | CCK-8 is used in the assay. MDA-MB-231 cells are cultured in 96-well plates at a density of 2 × 103 cells/well and then treated with DMSO vehicle or various concentrations of Betulinic acid ranging from 5 µM to 160 µM in 100 µL of medium for the indicated times. After the treatment period, the medium in each well is replaced with 110 µL of medium containing 10 µL of the CCK-8 mixture, and the plates are incubated for 1 h and 30 min at 37°C. The absorbance at a wavelength of 450 nm is measured with a microplate reader[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Female Swiss albino mice are administered vehicle (5% v/v DMSO in peanut oil) or Betulinic acid (3, 10 or 30 mg/kg) in vehicle, orally. After 1 h, acetic acid (300 mg/kg) is administered by intraperitoneal route and number of writhing response of each animal is counted for 20 min by an observer who is blind to the treatments. Writhing response is when animal rubs its abdomen on surface of table/floor with elongation of the body and extension of the hind limbs[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 550.0±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 295-298 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 456.700 |
| Flash Point | 300.5±21.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 456.360352 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 8.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 7 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Analysis of triterpenoids and phytosterols in vegetables by thin-layer chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1381 , 229-38, (2015) Three TLC methods were used for an initial screening of some common plant triterpenoids and phytosterols in cuticular wax extracts of different vegetables (zucchini, eggplant, tomato, red pepper, mang... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii.
Plant Cell Physiol. 56 , 1172-82, (2015) Mogrosides, the major bioactive components isolated from the fruits of Siraitia grosvenorii, are a family of cucurbitane-type tetracyclic triterpenoid saponins that are used worldwide as high-potency ... |
| (3β)-3-Hydroxylup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid |
| Gratiolone |
| (1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-9-Hydroxy-1-isopropenyl-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethylicosahydro-3aH-cyclopenta[a]chrysene-3a-carboxylic acid |
| betulic acid |
| Platanol |
| 3β-Hydroxy-20(29)-lupaene-28-oic Acid |
| (3b)-3-hydroxylup-20(29)-en-28-oic Acid |
| Lup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid, 3β-hydroxy- |
| Betulinic acid |
| MFCD00009619 |
| MAIRIN |
| Lup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid, 3-hydroxy-, (3β)- |
| Melaleucin |
| ALS-357 |
| EINECS 207-448-8 |
| Betulinic |
 CAS#:13159-28-9
CAS#:13159-28-9 CAS#:473-98-3
CAS#:473-98-3 CAS#:4481-62-3
CAS#:4481-62-3 CAS#:10376-50-8
CAS#:10376-50-8 CAS#:135757-66-3
CAS#:135757-66-3 CAS#:22333-85-3
CAS#:22333-85-3 CAS#:27570-20-3
CAS#:27570-20-3 CAS#:1125546-06-6
CAS#:1125546-06-6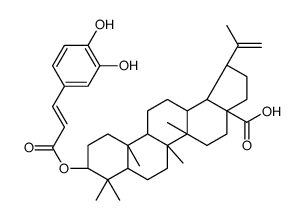 CAS#:80832-44-6
CAS#:80832-44-6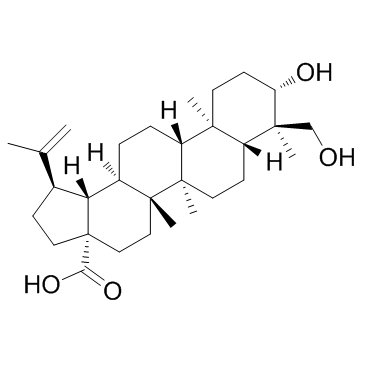 CAS#:85999-40-2
CAS#:85999-40-2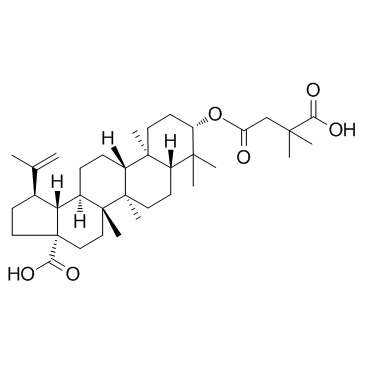 CAS#:174022-42-5
CAS#:174022-42-5![3-[[(1R,3aS,5aR,5bR,7aR,9S,11aR,11bR,13aR,13bR)-9-hydroxy-5a,5b,8,8,11a-pentamethyl-1-prop-1-en-2-yl-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,7a,9,10,11,11b,12,13,13a,13b-hexadecahydrocyclopenta[a]chrysene-3a-carbonyl]amino]propanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/305/174740-41-1.png) CAS#:174740-41-1
CAS#:174740-41-1 CAS#:2131-43-3
CAS#:2131-43-3
