H-Gly-Asp-OH
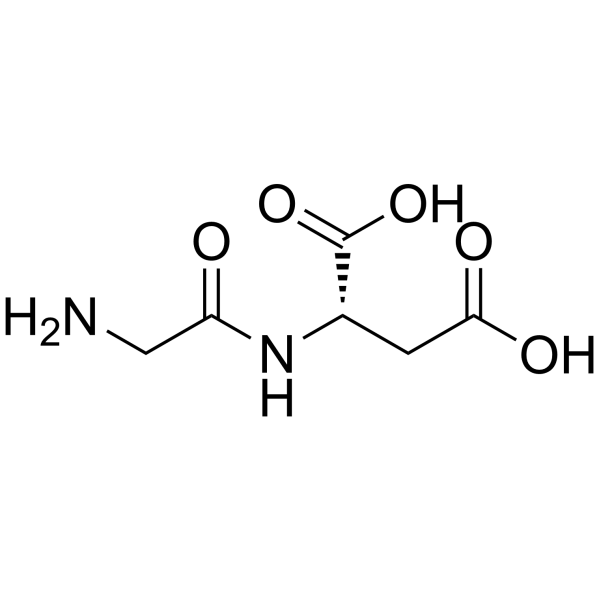
H-Gly-Asp-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-Gly-Asp-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4685-12-5 | Molecular Weight | 190.15400 | |
| Density | 1.499 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 468.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 | Melting Point | ~205 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 237.3ºC | |
Use of H-Gly-Asp-OHGly-Asp is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
| Name | glycyl-l-aspartic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Gly-Asp is a Glycine (HY-Y0966) derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.499 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 468.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | ~205 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 190.15400 |
| Flash Point | 237.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 190.05900 |
| PSA | 129.72000 |
| Index of Refraction | 13 ° (C=2, H2O) |
| Storage condition | -15°C |
|
~% 
H-Gly-Asp-OH CAS#:4685-12-5 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 32, # 12 p. 641 - 645 |
|
~% 
H-Gly-Asp-OH CAS#:4685-12-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Biological Chemistry, , vol. 176, p. 1300 |
|
~% 
H-Gly-Asp-OH CAS#:4685-12-5 |
| Literature: Archives of Biochemistry, , vol. 56, p. 11,13 |
|
~% 
H-Gly-Asp-OH CAS#:4685-12-5 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 91, p. 449,453 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Purification, characterization, and localization of aspartoacylase from bovine brain.
J. Neurochem. 56(1) , 129-35, (1991) Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive disorder, is characterized biochemically by N-acetylaspartic aciduria and aspartoacylase (N-acyl-L-aspartate amidohydrolase; EC 3.5.1.15) deficiency. However, t... |
|
|
Conformation and structure of acidic dipeptides. Crystal structure of glycyl-L-aspartic acid dihydrate.
Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 19(2) , 206-11, (1982) The crystal structure of the acidic dipeptide glycyl-L-aspartic acid dihydrate, Gly-L-Asp X 2H2O, C6H10N2O5 X 2H2O, has been determined by means of three-dimensional counter X-ray data. The dipeptide ... |
|
|
Reduction of vanadium(V) to vanadium(IV) by NADPH, and vanadium(IV) to vanadium(III) by cysteine methyl ester in the presence of biologically relevant ligands.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1770(8) , 1212-8, (2007) To better understand the mechanism of vanadium reduction in ascidians, we examined the reduction of vanadium(V) to vanadium(IV) by NADPH and the reduction of vanadium(IV) to vanadium(III) by L-cystein... |
| Gly-L-Asp-OH |
| GLY-ASP |
| Glycyl-L-aspartic acid dihydrate |
| H-Gly-Asp-OH |
| Gly-Asp dihydrate |
| glycylaspartic acid |
| H-Gly-Asp-OH Monohydrate |
| EINECS 225-140-1 |
| Glycyl-L-aspartic Acid Monohydrate |
| L-Aspartic acid,N-glycyl |
| Gly-Asp-OH |
| dlycyl-L-aspartic acid |
| (S)-2-(2-Aminoacetamido)succinic acid |
| MFCD00025585 |
![2-[(2-chloroacetyl)amino]butanedioic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/493/67036-33-3.png)


 CAS#:56-84-8
CAS#:56-84-8 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6 CAS#:99896-85-2
CAS#:99896-85-2
