DL-Valine
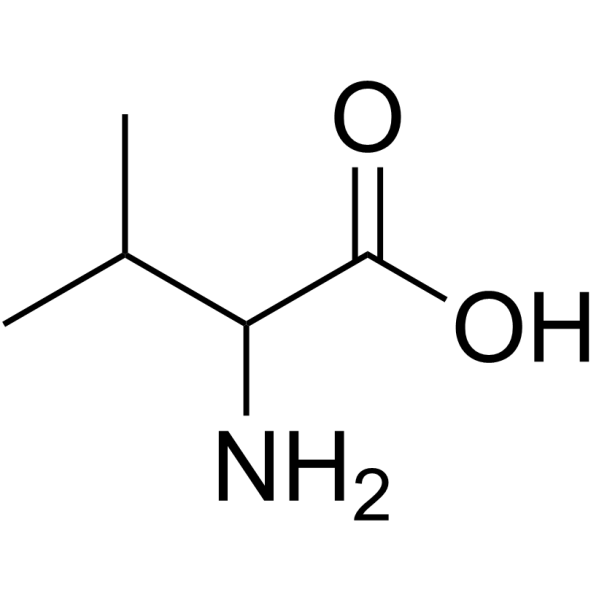
DL-Valine structure
|
Common Name | DL-Valine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 516-06-3 | Molecular Weight | 117.146 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 213.6±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 | Melting Point | 283.5-285ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 83.0±22.6 °C | |
Use of DL-ValineDL-Valine is a valine derivative[1]. |
| Name | valine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Valine is a valine derivative[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Amino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 213.6±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 283.5-285ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 117.146 |
| Flash Point | 83.0±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 117.078979 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 0.20 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.461 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | 68 g/L |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Bee pollen improves muscle protein and energy metabolism in malnourished old rats through interfering with the Mtor signaling pathway and mitochondrial activity.
Nutrients 6(12) , 5500-16, (2014) Although the management of malnutrition is a priority in older people, this population shows a resistance to refeeding. Fresh bee pollen contains nutritional substances of interest for malnourished pe... |
|
|
¹H-NMR and MS based metabolomics study of the intervention effect of curcumin on hyperlipidemia mice induced by high-fat diet.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0120950, (2015) Curcumin, a principle bioactive component of Curcuma longa L, is well known for its anti-hyperlipidemia effect. However, no holistic metabolic information of curcumin on hyperlipidemia models has been... |
|
|
A DNA-scaffolded silver nanocluster/Cu²⁺ ensemble as a turn-on fluorescent probe for histidine.
Analyst 139(12) , 3122-6, (2014) A new type of rapid, sensitive, and selective fluorescence turn-on assay was developed for detection of histidine using a DNA-scaffolded silver nanocluster/Cu(2+) ensemble (DNA-AgNC/Cu(2+)). Cu(2+) wa... |
| Val |
| NH2CH(CO2H)iPr |
| H-DL-Val-OH |
| EINECS 208-220-0 |
| (RS)-Valine |
| 2-aminoisovaleric acid |
| Valine,DL |
| DL-a-Aminoisovaleric Acid |
| DL-.α.-Aminoisovaleric acid |
| DL-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid |
| Valine (9CI) |
| (R,S)-valine |
| 2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid, DL- |
| 2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid (VAN) |
| α-aminoisovaleric acid |
| MFCD00004267 |
| aminoisobutylic acid |
| FEMA 3444 |
| 2-Amino-3-methylbutyric acid |
| 2-Amino-3-methylbutyric acid, DL- |
| D,L-Valine |
| DL-Valine |
| (±)-Valine |
| 2-Aminoisovaleric acid, DL- |
| DL-Val |
| Butanoic acid, 2-amino-3-methyl- |
| Valine |
| DL-2-Amino-3-methylbutyric acid |
| DL-2-Aminoisovaleric acid |
| (±)-α-Aminoisovaleric acid |
 CAS#:759-05-7
CAS#:759-05-7 CAS#:70591-23-0
CAS#:70591-23-0 CAS#:73405-08-0
CAS#:73405-08-0 CAS#:72-18-4
CAS#:72-18-4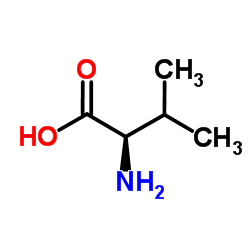 CAS#:640-68-6
CAS#:640-68-6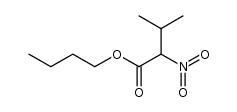 CAS#:106306-43-8
CAS#:106306-43-8 CAS#:495-69-2
CAS#:495-69-2 CAS#:67-64-1
CAS#:67-64-1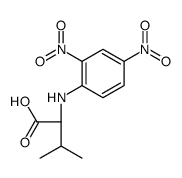 CAS#:10547-33-8
CAS#:10547-33-8 CAS#:111421-95-5
CAS#:111421-95-5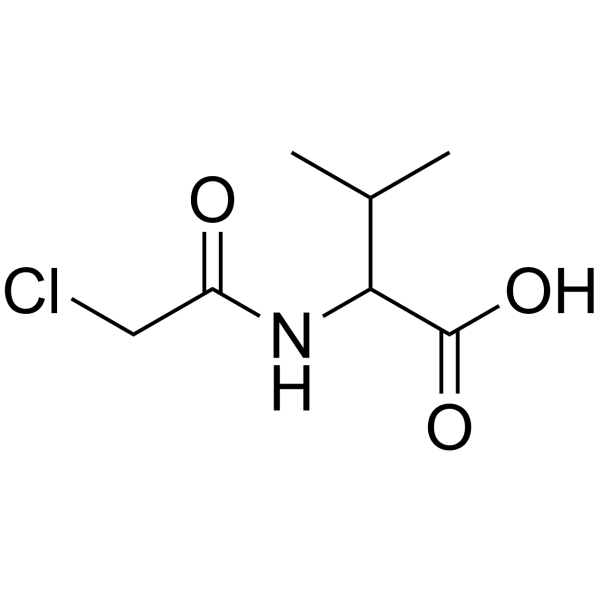 CAS#:4090-17-9
CAS#:4090-17-9 CAS#:4289-97-8
CAS#:4289-97-8 CAS#:55-21-0
CAS#:55-21-0 CAS#:78-84-2
CAS#:78-84-2 CAS#:4026-18-0
CAS#:4026-18-0 CAS#:4333-20-4
CAS#:4333-20-4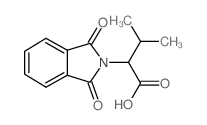 CAS#:5115-65-1
CAS#:5115-65-1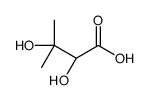 CAS#:19451-56-0
CAS#:19451-56-0
