Galangin
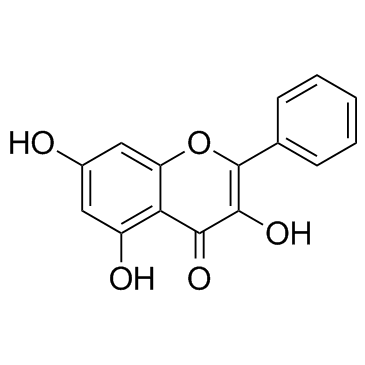
Galangin structure
|
Common Name | Galangin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 548-83-4 | Molecular Weight | 270.237 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 518.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 | Melting Point | 214-215 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 202.0±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of GalanginGalangin is an agonist/antagonist of the arylhydrocarbon receptor, and also shows inhibition of CYP1A1 activity. |
| Name | galangin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Galangin is an agonist/antagonist of the arylhydrocarbon receptor, and also shows inhibition of CYP1A1 activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Galangin inhibits the catabolic breakdown of DMBA, as measured by thin-layer chromatography, in a dose-dependent manner. Galangin also inhibits the formation of DMBA-DNA adducts, and prevents DMBA-induced inhibition of cell growth. Galangin causes a potent, dose-dependent inhibition of CYP1A1 activity, as measured by ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity, in intact cells and in microsomes isolated from DMBA-treated cells. Analysis of the inhibition kinetics by double-reciprocal plot demonstrates that galangin inhibits CYP1A1 activity in a noncompetitive manner. Galangin causes an increase in the level of CYP1A1 mRNA, indicating that it may be an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, but it inhibits the induction of CYP1A1 mRNA by DMBA or by 2,3,5,7-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Galangin also inhibits the DMBA- or TCDD-induced transcription of a reporter vector containing the CYP1A1 promoter[1]. Galangin treatment inhibits cell proliferation and induced autophagy (130 μM) and apoptosis (370 μM). In particular, galangin treatment in HepG2 cells causes (1) an accumulation of autophagosomes, (2) elevated levels of microtubule-associated protein light chain 3, and (3) an increased percentage of cells with vacuoles. p53 expression is also increased. The galangin-induced autophagy is attenuated by the inhibition of p53 in HepG2 cells, and overexpression of p53 in Hep3B cells restored the galangin-induced higher percentage of cells with vacuoles to normal level[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells (5.0×103) are seeded and treated with different concentrations of galangin for different periods of time in 96-well plates. The number of viable cells in each well is determined by adding 10 µL of 5 mg/mL MTT solution. Following the 4 hour incubation at 37°C, the cells are dissolved in a 100 µL solution containing 20% SDS and 50% dimethy formamide. The optical densities are quantified at a test wavelength of 570 nm with a reference wavelength of 630 nm using a Varioskan Flash Reader spectrophotometer. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 518.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 214-215 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.237 |
| Flash Point | 202.0±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.052826 |
| PSA | 90.90000 |
| LogP | 2.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.748 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LK9275500 |
| HS Code | 2914400090 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2914400090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914400090 other ketone-alcohols and ketone-aldehydes。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Protective Effect of Plantago major Extract against t-BOOH-Induced Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage and Cytotoxicity.
Molecules 20 , 17747-59, (2015) Plantago major L. produces several chemical substances with anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities and its use in the treatment of oral and throat inflammation in popular medicine is well describe... |
|
|
Ultra high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of phenolic constituents in honey from various floral sources using multiwalled carbon nanotubes as extraction sorbents.
J. Sep. Sci. 38 , 2597-606, (2015) An ultra high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry method has been developed for the simultaneous separation, identification and determination of 22 phenolic constituents in honey ... |
|
|
Combined experimental and in silico approaches for exploring antiperoxidative potential of structurally diverse classes of antioxidants on docetaxel-induced lipid peroxidation using 4-HNE as the model marker.
Bioorg. Chem. 56 , 1-7, (2014) The objective of the present work was tantamount to explain the antiperoxidative potential and structural requirements of twenty-eight structurally diverse classes of antioxidants on docetaxel-induced... |
| EINECS 208-960-4 |
| 3,5,7-trihydroxyflavone |
| Galangin |
| teptochrysin |
| Galengin |
| 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-phenyl-chromen-4-one |
| 3,5,7-trihydroxy-flavon |
| 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one |
| 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-Flavone |
| galangine |
| 5,7-dihydroxyflavonol |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-phenyl- |
| NORIZALPININ |
| 3,5,7-trihydroxyfalvone |
| MFCD00006833 |
| 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
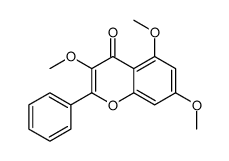 CAS#:26964-29-4
CAS#:26964-29-4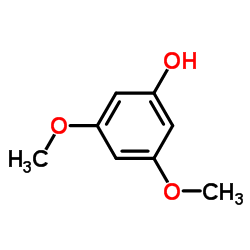 CAS#:500-99-2
CAS#:500-99-2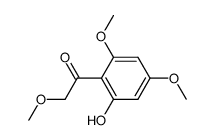 CAS#:17874-42-9
CAS#:17874-42-9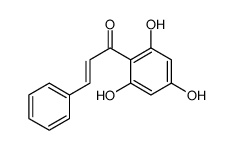 CAS#:82451-30-7
CAS#:82451-30-7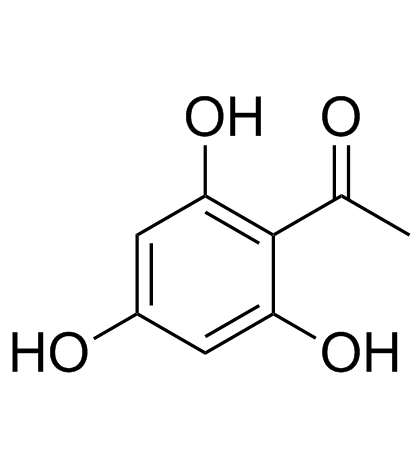 CAS#:480-66-0
CAS#:480-66-0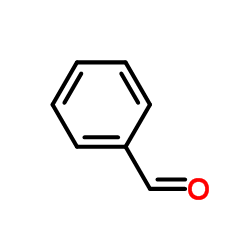 CAS#:100-52-7
CAS#:100-52-7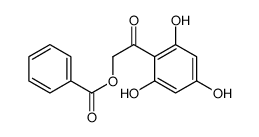 CAS#:65982-77-6
CAS#:65982-77-6 CAS#:93-97-0
CAS#:93-97-0 CAS#:487-70-7
CAS#:487-70-7 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0 CAS#:1707-75-1
CAS#:1707-75-1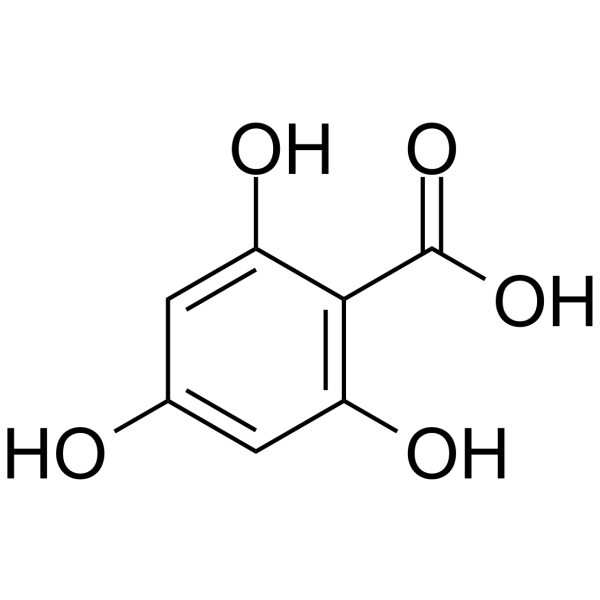 CAS#:83-30-7
CAS#:83-30-7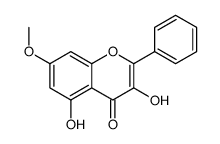 CAS#:480-14-8
CAS#:480-14-8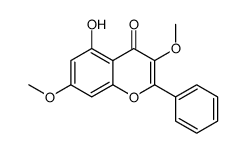 CAS#:70786-48-0
CAS#:70786-48-0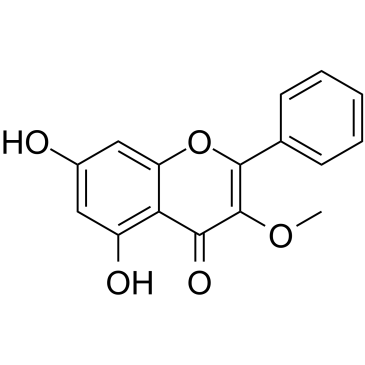 CAS#:6665-74-3
CAS#:6665-74-3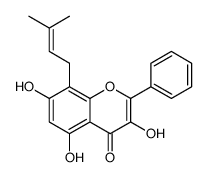 CAS#:42193-83-9
CAS#:42193-83-9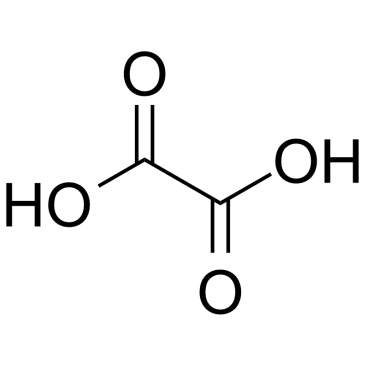 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7
