Acetylcholine chloride
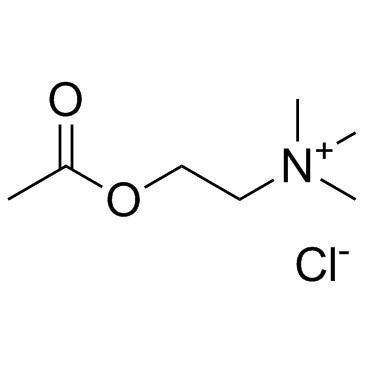
Acetylcholine chloride structure
|
Common Name | Acetylcholine chloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60-31-1 | Molecular Weight | 181.660 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H16ClNO2 | Melting Point | 146-150 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Acetylcholine chlorideAcetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels. Target: Calcium Channel; nAChR; mAChRAcetylcholine in vertebrates is the major transmitter at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. It is generally not used as an administered drug because it is broken down very rapidly by cholinesterases, but it is useful in some ophthalmological applications.Acetylcholine chloride, more commonly referred to as just acetylcholine, is a cholinergic neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels, as well as act on nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholine plays an important role at many sites in the central nervous system. The compound has been shown to have ophthalmological uses and can be broken down quickly by choliesterases. Studies show that non-neuronal acetylcholine influences many basic cells functions, such as mitosis, cells differentiation, cytoskeletal organization, and cell to cell contact, among other functions [1-3]. |
| Name | acetylcholine chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels. Target: Calcium Channel; nAChR; mAChRAcetylcholine in vertebrates is the major transmitter at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. It is generally not used as an administered drug because it is broken down very rapidly by cholinesterases, but it is useful in some ophthalmological applications.Acetylcholine chloride, more commonly referred to as just acetylcholine, is a cholinergic neurotransmitter that can induce the opening of calcium channels, as well as act on nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholine plays an important role at many sites in the central nervous system. The compound has been shown to have ophthalmological uses and can be broken down quickly by choliesterases. Studies show that non-neuronal acetylcholine influences many basic cells functions, such as mitosis, cells differentiation, cytoskeletal organization, and cell to cell contact, among other functions [1-3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Melting Point | 146-150 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H16ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 181.660 |
| Exact Mass | 181.086960 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| Stability | Stable. Substances to be avoided include strong oxidizing agents. Protect from moisture - very hygroscopic. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | FZ9800000 |
| HS Code | 29379000 |
|
~% 
Acetylcholine c... CAS#:60-31-1 |
| Literature: Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi, , vol. 23, p. 456,458 Chem.Abstr., , p. 2696 |
|
~% 
Acetylcholine c... CAS#:60-31-1 |
| Literature: Archiv der Pharmazie (Weinheim, Germany), , vol. 232, p. 266 Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 142, p. 325 |
|
~% 
Acetylcholine c... CAS#:60-31-1 |
| Literature: Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France, , vol. <4>15, p. 547 |
|
~% 
Acetylcholine c... CAS#:60-31-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 52, # 8 p. 1613 - 1615 |
|
~% 
Acetylcholine c... CAS#:60-31-1 |
| Literature: Canadian Journal of Chemistry, , vol. 88, # 10 p. 1009 - 1016 |
| HS Code | 2923900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2923900090 other quaternary ammonium salts and hydroxides。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Choline partially prevents the impact of ethanol on the lipid raft dependent functions of l1 cell adhesion molecule.
Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 38(11) , 2722-30, (2014) Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, the leading known cause of mental retardation, is caused by alcohol exposure during pregnancy. One mechanism of ethanol (EtOH) teratogenicity is the disruption of the ... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| Acetylcholine chloride |
| 2-Acetoxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride |
| ethanaminium, 2-(acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethyl-, chloride |
| chlorure de 2-(acétyloxy)-N,N,N-triméthyléthanaminium |
| Ovisot |
| Acecoline |
| EINECS 200-468-8 |
| MFCD00011698 |
| Ethanaminium, 2-(acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| Arterocoline |
| 2-(acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride |
| Acetylcholine chloride,2-(Acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminiumchloride |
| 2-(Acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminiumchlorid |
| Acetylcholinium chloride |
| Acetylcholine (chloride) |




![L-Tryptophan,N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-L-tryptophyl-, methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/116/72254-56-9.png)

