Bifonazole
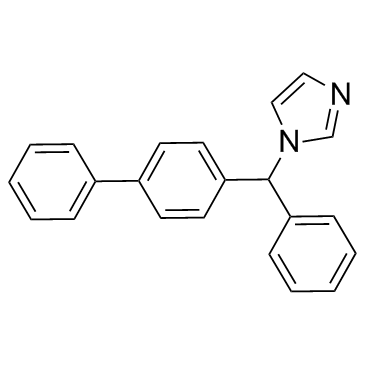
Bifonazole structure
|
Common Name | Bifonazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 60628-96-8 | Molecular Weight | 310.392 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 491.7±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18N2 | Melting Point | 142℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 251.2±22.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of BifonazoleBifonazole is an imidazole antifungal drug.Target: AntifungalBifonazole, a new broad-spectrum antimycotic, interferes with sterol biosynthesis. In dermatophytes bifonazole additionally inhibits directly HMG-CoA-reductase. bifonazole possesses a sequential mode of action, namely inhibition of cytochrome P450-dependent C14-demethylation of sterols and direct inhibition of HMG-CoA-reductase. In vitro bifonazole shows a strongly pH-dependent efficacy. The uptake kinetics of bifonazole have been measured with different pathogens [1]. Bifonazole additionally leads to a generally decreased rate of sterol biosynthesis as compared to clotrimazole, due to a direct inhibition of microsomal HMG-CoA-reductase. The additional fungicidal effects of bifonazole are considered to originate from a sequential action by inhibition of HMG-CoA-reductase and of cytochrome P450 [2]. bifonazole were affected by choice of medium with Kimmig's agar generally giving the lowest MIC's. Bifonazole MICs were shown to vary with pH (maximal activity at pH 6 . 5) with selected yeasts when tested on Kimmig's agar [3]. |
| Name | 1-[phenyl-(4-phenylphenyl)methyl]imidazole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bifonazole is an imidazole antifungal drug.Target: AntifungalBifonazole, a new broad-spectrum antimycotic, interferes with sterol biosynthesis. In dermatophytes bifonazole additionally inhibits directly HMG-CoA-reductase. bifonazole possesses a sequential mode of action, namely inhibition of cytochrome P450-dependent C14-demethylation of sterols and direct inhibition of HMG-CoA-reductase. In vitro bifonazole shows a strongly pH-dependent efficacy. The uptake kinetics of bifonazole have been measured with different pathogens [1]. Bifonazole additionally leads to a generally decreased rate of sterol biosynthesis as compared to clotrimazole, due to a direct inhibition of microsomal HMG-CoA-reductase. The additional fungicidal effects of bifonazole are considered to originate from a sequential action by inhibition of HMG-CoA-reductase and of cytochrome P450 [2]. bifonazole were affected by choice of medium with Kimmig's agar generally giving the lowest MIC's. Bifonazole MICs were shown to vary with pH (maximal activity at pH 6 . 5) with selected yeasts when tested on Kimmig's agar [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Berg, D. and M. Plempel, Bifonazole, a biochemist's view. Dermatologica, 1984. 169 Suppl 1: p. 3-9. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 491.7±24.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 142℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 310.392 |
| Flash Point | 251.2±22.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 310.147003 |
| PSA | 17.82000 |
| LogP | 4.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.616 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | NI3517000 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|
~95% 
Bifonazole CAS#:60628-96-8 |
| Literature: Corelli; Summa; Brogi; Monteagudo; Botta Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1995 , vol. 60, # 7 p. 2008 - 2015 |
|
~% 
Bifonazole CAS#:60628-96-8 |
| Literature: US4118487 A1, ; |
|
~% 
Bifonazole CAS#:60628-96-8 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 60, # 7 p. 2008 - 2015 |
|
~% 
Bifonazole CAS#:60628-96-8 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 60, # 7 p. 2008 - 2015 |
|
~11% 
Bifonazole CAS#:60628-96-8 |
| Literature: Hu, Qingzhong; Negri, Matthias; Jahn-Hoffmann, Kerstin; Zhuang, Yan; Olgen, Sureyya; Bartels, Marc; Mueller-Vieira, Ursula; Lauterbach, Thomas; Hartmann, Rolf W. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2008 , vol. 16, # 16 p. 7715 - 7727 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
The effect of topically applied antimycotic agents on inner ear vestibular and cochlear function.
Laryngoscope 123(4) , 1033-9, (2013) To assess and compare the effect of commonly used topical antimycotic agents and their solvents on the function of the vestibular and cochlear parts of the sand rat's inner ear.Prospective, controlled... |
|
|
Factors influencing crystal growth rates from undercooled liquids of pharmaceutical compounds.
J. Phys. Chem. B 118(33) , 9974-82, (2014) Amorphous forms of drugs are increasingly being used to deliver poorly water-soluble compounds. Therefore, understanding the magnitude and origin of differences in crystallization kinetics is highly i... |
|
|
A method to identify and validate mitochondrial modulators using mammalian cells and the worm C. elegans.
Sci. Rep. 4 , 5285, (2014) Mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles regulated by a complex network of proteins that are vital for many cellular functions. Because mitochondrial modulators can impact many aspects of cellular ... |
| Bifonazole |
| 1-[PHENYL-(4-PHENYLPHENYL)-METHYL]IMIDAZOLE |
| rac-bifonazole |
| (±)-Bifonazole |
| (biphenyl-4-yl)phenyl-imidazol-1-ylmethane |
| 1-[4-Biphenylyl(phenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole |
| Canespor |
| 1H-Imidazole, 1-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-ylphenylmethyl)- |
| Bifonazol [INN-Spanish] |
| Azolmen |
| Trifonazole |
| EINECS 262-336-6 |
| BAY H 4502 |
| 1-[biphenyl-4-yl(phenyl)methyl]imidazole |
| Amycor |
| 1-[biphenyl-4-yl(phenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole |
| 1-[Biphenyl-4-yl(phenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazol |
| Bifazol |
| 1-(biphenyl-4-yl-phenyl-methyl)-1H-imidazole |
| (±)-1-(p,a-Diphenylbenzyl)imidazole |
| 1-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-ylphenylmethyl)-1H-imidazole |
| Bifonazol |
| Mycospor |
| Bifonazolum |
| MFCD00865567 |