CHRYSAMINE G
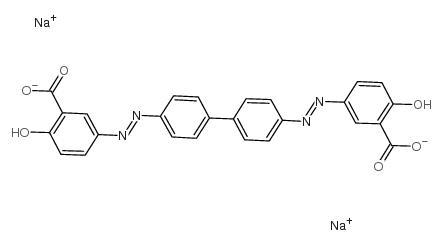
CHRYSAMINE G structure
|
Common Name | CHRYSAMINE G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6472-91-9 | Molecular Weight | 526.40800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 711.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H16N4Na2O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 384ºC | |
Use of CHRYSAMINE GChrysamine G, a carboxylic acid analogue of Congo Red, can be used as a probe of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Chrysamine G also can inhibit Aβ-induced toxicity in PC12 cells[1][2]. |
| Name | chrysamine g |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Chrysamine G, a carboxylic acid analogue of Congo Red, can be used as a probe of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Chrysamine G also can inhibit Aβ-induced toxicity in PC12 cells[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 711.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H16N4Na2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 526.40800 |
| Flash Point | 384ºC |
| Exact Mass | 526.08700 |
| PSA | 170.16000 |
| LogP | 4.32260 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 
CHRYSAMINE G CAS#:6472-91-9 |
| Literature: European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 38, # 6 p. 567 - 579 |
|
~% 
CHRYSAMINE G CAS#:6472-91-9 |
| Literature: Trans.electroch.Soc., , vol. 75, p. 377,381 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiphoton microscopy and methoxy-X04, a systemically administered Congo red derivative.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002) The identification of amyloid deposits in living Alzheimer disease (AD) patients is important for both early diagnosis and for monitoring the efficacy of newly developed anti-amyloid therapies. Methox... |
|
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002) Extracellular senile plaques (SPs) are hallmark brain lesions of sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the likely consequence of genetic mutations that cause familial AD by increasing production of am... |
|
|
Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity in mice.
Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002) The neurotoxicity of amyloid beta (Abeta) is widely believed to play a seminal role in neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. We examined the effect of Chrysamine G (CG) on such neurotoxicity using... |
| C.I.Direct Yellow 1 |
| Chrysamin-G |
| CHRYSAMINE |
| 6,6'-dihydroxy-3,3'-biphenyl-4,4'-diyl-bis-azo-dibenzoic acid disodium salt |
| 6,6'-Dihydroxy-3,3'-biphenyl-4,4'-diylbisazo-di-benzoesaeure,Dinatrium-Salz |