L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride

L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 657-27-2 | Molecular Weight | 182.648 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 311.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H15ClN2O2 | Melting Point | 263 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 142.2ºC | |
Use of L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochlorideL-lysine hydrochloride is an essential amino acid for humans with various benefits including treating herpes, increasing calcium absorption, reducing diabetes-related illnesses and improving gut health. |
| Name | L-lysine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-lysine hydrochloride is an essential amino acid for humans with various benefits including treating herpes, increasing calcium absorption, reducing diabetes-related illnesses and improving gut health. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | L-lysine treatment attenuates pancreatic tissue injury induced by L-arginine by inhibiting the release of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and enhances antioxidant activity. Pre- or post-treatment with L-lysine leads to significant decreases in the levels of malondialdehyde and nitric oxide, while significant enhancement is observed in the activities of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) and glutathione[1]. L-lysine supplementation almost completely ameliorates vascular calcification. Dietary L-lysine strongly suppresses plasma intact parathyroid hormone in adenine rats and supports a proper bone-vascular axis. The conserved orientation of the femoral apatite in group Lys also evidences the bone-protective effects of L-lysine. Dietary L-lysine elevates plasma alanine, proline, arginine, and homoarginine but not lysine[2]. The dose-dependent delay in gastric emptying observed in rats is confirmed in humans with an increase in halftime of gastric emptying of 4 min/g L-lysine. Moreover, a dose-dependent increase in intestinal fluid accumulation is observed (0.4 mL/min/g L-lysine)[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Nephrocalcinosis in 6-week-old male Wistar rats is induced by continuous injection of rat PTH 1-34 at a dosage of 40 μg/kg per day via an osmotic mini-pump for 50 hours. L-lysine HCl or glycine at a dose of 20 mmol/kg is administered via a gastric tube at 2 hours, 14 hours, 26 hours, and 38 hours after the implantation of the osmotic pump. At the indicated periods, Serum and urinary biochemical parameters, urea nitrogen, albumin, calcium, inorganic phosphate, and magnesium are determined by clinical diagnostic reagents[2]. Mice: Four groups of mice (10 in each group) are assessed. Group I is the control. Animals in groups II-IV are injected intraperitoneally with L-arginine hydrochloride (400 mg/kg body weight [bw]) for 3 days. Group III animals are orally pre-treated with L-lysine(10 mg/kg bw), whereas group IV animals are orally post-treated with L-lysine(10 mg/kg bw). Serum samples are subjected to amylase, lipase, transaminase, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) assays. The pancreas is excised to measure the levels of malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, catalase, superoxide dismutase, reduced glutathione, and glutathione peroxidase[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 311.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 263 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H15ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.648 |
| Flash Point | 142.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 182.082199 |
| PSA | 89.34000 |
| LogP | 1.72990 |
| Water Solubility | 65 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 1789 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | OL5650000 |
| HS Code | 29224100 |
|
~99% 
L-(+)-Lysine mo... CAS#:657-27-2 |
| Literature: Adamczeski,M.; Quinoa,E.; Crews,P. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1989 , vol. 111, p. 647 |
|
~78% 
L-(+)-Lysine mo... CAS#:657-27-2 |
| Literature: Raap, J.; Wielen, C. M. van der; Lugtenburg, J. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1990 , vol. 109, # 4 p. 277 - 286 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Lysine mo... CAS#:657-27-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 111, p. 647 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Lysine mo... CAS#:657-27-2 |
| Literature: Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, , vol. 109, # 4 p. 277 - 286 |
|
~% 
L-(+)-Lysine mo... CAS#:657-27-2
Detail
|
| Literature: Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, , vol. 54, # 12 p. 3275 - 3282 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Salicylic acid signaling controls the maturation and localization of the arabidopsis defense protein ACCELERATED CELL DEATH6.
Mol. Plant 7(8) , 1365-83, (2014) ACCELERATED CELL DEATH6 (ACD6) is a multipass membrane protein with an ankyrin domain that acts in a positive feedback loop with the defense signal salicylic acid (SA). This study implemented biochemi... |
|
|
Gene transfer of high-mobility group box 1 box-A domain in a rat acute liver failure model.
J. Surg. Res. 194(2) , 571-80, (2015) High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) has recently been identified as an important mediator of various kinds of acute and chronic inflammation. The protein encoded by the box-A domain of the HMGB1 gene is... |
|
|
DNase II-dependent DNA digestion is required for DNA sensing by TLR9.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 5853, (2015) DNase II digests DNA in endolysosomes. In the absence of DNase II, undigested DNA activates cytoplasmic DNA-sensing pathways. Little is known, however, about the role of DNase II in endolysosomal DNA ... |
| H-Lys-OH.HCl |
| MFCD00064564 |
| L-Lysinehydrochloride |
| (2S)-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid monohydrochloride |
| L-Lysine, monohydrochloride |
| L-LYS HCL |
| Lysine hydrochloride |
| L-Lysine HCl |
| LYSINE-L HCL |
| L-Lysine hydrochloride |
| LYS,HCL |
| anhydrous L-lysine monohydrochloride |
| EINECS 211-519-9 |
| L-Lysine, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| (S)-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid monohydrochloride |
| H-Lys-OH hydrochloride |
| (S)-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid hydrochloride |
| L-Lysine chlorhydrate |
| L-Lysine, hydrochloride |
| LYSINE HCL |
| (2S)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid hydrochloride |
| L-Lysine hydrochloride (1:1) |
![4-[(2R,5S)-2,5-Dihydro-2-isopropyl-3,6-dimethoxy-5-pyrazinyl]butylamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/114/129243-87-4.png)

![4-[(2R,5S)-2,5-Dihydro-2-isopropyl-3,6-dimethoxy-5-pyrazinyl]butyronitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/266/129243-83-0.png)

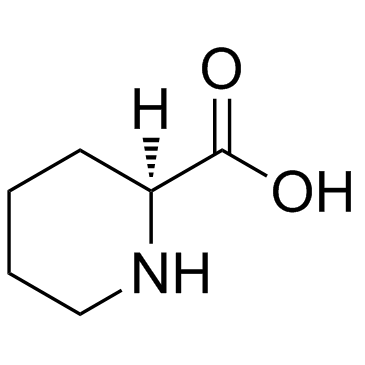 CAS#:3105-95-1
CAS#:3105-95-1![N2-[(Benzyloxy)Carbonyl]-N6-(Trifluoroacetyl)-L-Lysine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/165/14905-30-7.png) CAS#:14905-30-7
CAS#:14905-30-7 CAS#:405-39-0
CAS#:405-39-0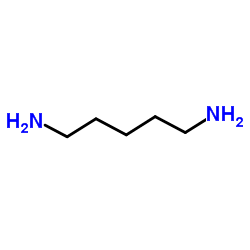 CAS#:462-94-2
CAS#:462-94-2 CAS#:42457-10-3
CAS#:42457-10-3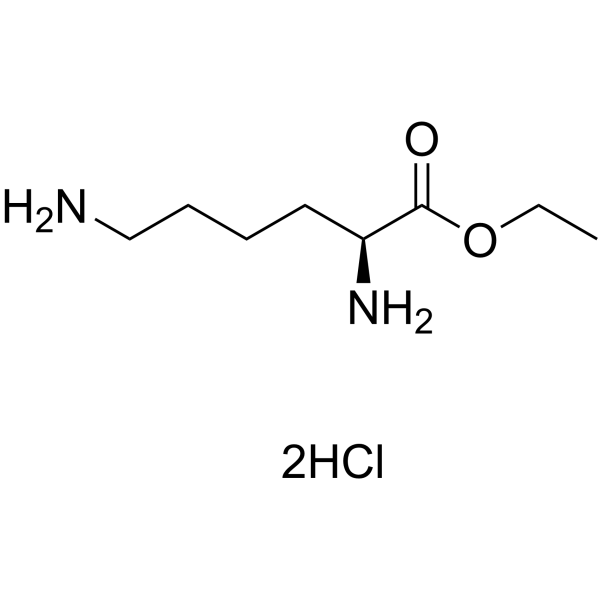 CAS#:3844-53-9
CAS#:3844-53-9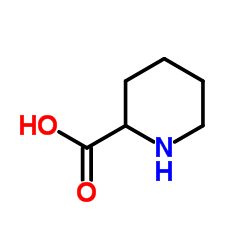 CAS#:4043-87-2
CAS#:4043-87-2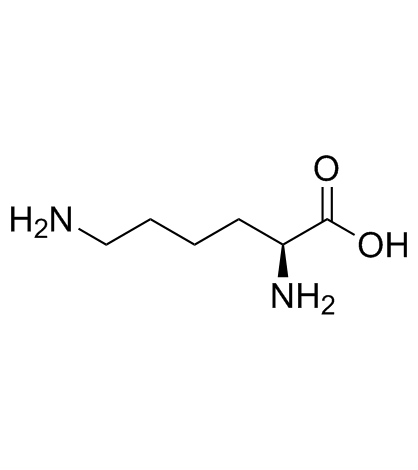 CAS#:56-87-1
CAS#:56-87-1 CAS#:675-20-7
CAS#:675-20-7
