Citric Acid
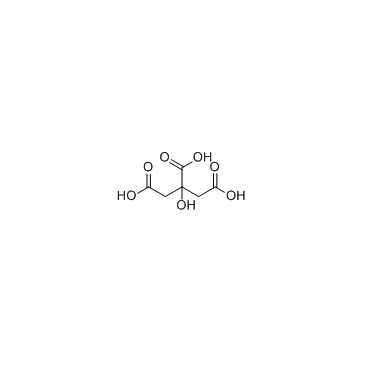
Citric Acid structure
|
Common Name | Citric Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 77-92-9 | Molecular Weight | 192.124 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 309.6±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O7 | Melting Point | 153-159 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 155.2±24.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Citric AcidCitric acid is a weak organic tricarboxylic acid found in citrus fruits. Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer. |
| Name | citric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Citric acid is a weak organic tricarboxylic acid found in citrus fruits. Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Citric acid induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. It inhibits proliferation of HaCaT cells in a dose-dependent manner, but also induces apoptosis and cell cycle-arrest at the G2/M phase (before 24 h) and S phase (after 24 h)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Citric acid is found in all animal tissues as an intermediary substance in oxidative metabolism. The administration of citric acid (1–2 g/kg) attenuates LPS-induced elevations in brain MDA, nitrite, TNF-α, GPx, and PON1 activity. In the liver, nitrite is decreased by 1 g/kg citric acid. Citric acid (1-2 g/kg) decreases brain lipid peroxidation and inflammation, liver damage, and DNA fragmentation[2]. Citric acid supplementation increases intestinal calcium and phosphorus absorption and the retention/intake ratio only in rats fed the 1% Ca diet. Citric acidsupplementation together with a calcium-rich diet allows to obtain an increased retention of calcium and phosphorus in bone. The prolonged administration of calcium citrate supplements may therefore help to increase bone mineral concentration[3]. Oral administration of citric acid ameliorates ketosis and protects against the development of diabetic complications in an animal model of type 1 diabetes[4]. |
| Cell Assay | HaCaT cells are treated with different concentrations of citric acid (2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5 mM) for 24 h; 0.5% of DMSO (vehicle) is used as a control. Cells are then centrifuged at 1000 ×g for 5 min, and cell pellets are dissolved with 0.5 mL of Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 5 μg/mL PI and viable cells are determined by using a flow cytometer for determination of viable cells[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rats are induced of diabetes and divided randomly into an untreated diabetic group and two treated diabetic groups, receiving citric acid (2 g/L) in the drinking water, or insulin therapy. Insulin-treated rats receive 3 IU of neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin three times per week. Fasting (12 hr) blood samples are obtained from the tail vein two days after insulin injection for measurement of blood glucose, HbA1c and ketone bodies[4]. [2]Mice: Citric acid is prepared in sterile physiological saline. Mice are randomly divided into five equal groups (six mice each). Mice are treated with either 0.2mL of: sterile physiological saline (group 1) or citric acid at doses of 1, 2, and 4 g/kg, orally (groups 2-4). Treatments are given just prior to endotoxin administration (LPS: 200 lg/kg, injected intraperitoneally, 0.1 mL). The fifth group received just the vehicle, no LPS (negative control). Mice are euthanized after 4 h of LPS or vehicle injection by decapitation under ether anesthesia, where the brain and liver of each mouse are then removed for analysis[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 309.6±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 153-159 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 192.124 |
| Flash Point | 155.2±24.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 192.027008 |
| PSA | 132.13000 |
| LogP | -1.72 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.575 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with bases, strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, metal nitrates. |
| Water Solubility | 750 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S39-S37/39-S24/25-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1789 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | GE7350000 |
| HS Code | 2918140000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918140000 |
|---|
|
Disruption of an M. tuberculosis membrane protein causes a magnesium-dependent cell division defect and failure to persist in mice.
PLoS Pathog. 11(2) , e1004645, (2015) The identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes necessary for persistence in vivo provides insight into bacterial biology as well as host defense strategies. We show that disruption of M. tuber... |
|
|
Ultrastructural morphologic changes in mycobacterial biofilm in different extreme condition.
Ultrastruct. Pathol. 39(1) , 38-48, (2015) The aim of this study was to investigate the morphologic and ultrastructural features of biofilms of slow and fast-growing mycobacteria in different stress conditions, presence and absence of oleic ac... |
|
|
Accurate analysis of ginkgolides and their hydrolyzed metabolites by analytical supercritical fluid chromatography hybrid tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1388 , 251-8, (2015) Hydrolysis plays an important role in the metabolic transformations of lactones. Analysis of lactones and their hydrolyzed metabolites in biological samples is challenging, because unexpected hydrolys... |
| 3'-hydroxybiphenyl-3-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00163176 |
| 3-hydroxy-3-carboxy-pentanedioic acid |
| 3'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid |
| Citric acid |
| EINECS 201-069-1 |
 CAS#:533-76-6
CAS#:533-76-6 CAS#:77182-75-3
CAS#:77182-75-3 CAS#:87216-17-9
CAS#:87216-17-9 CAS#:50-99-7
CAS#:50-99-7 CAS#:57-50-1
CAS#:57-50-1 CAS#:36838-71-8
CAS#:36838-71-8 CAS#:61565-18-2
CAS#:61565-18-2 CAS#:133-99-3
CAS#:133-99-3 CAS#:1830-54-2
CAS#:1830-54-2![2-[5-oxo-4-(2-oxo-2-prop-2-enoxyethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/284/110333-20-5.png) CAS#:110333-20-5
CAS#:110333-20-5 CAS#:32328-03-3
CAS#:32328-03-3 CAS#:5990-32-9
CAS#:5990-32-9 CAS#:498-23-7
CAS#:498-23-7 CAS#:97-65-4
CAS#:97-65-4 CAS#:499-12-7
CAS#:499-12-7 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7 CAS#:79-33-4
CAS#:79-33-4 CAS#:10326-41-7
CAS#:10326-41-7
