Pseudolaric acid B
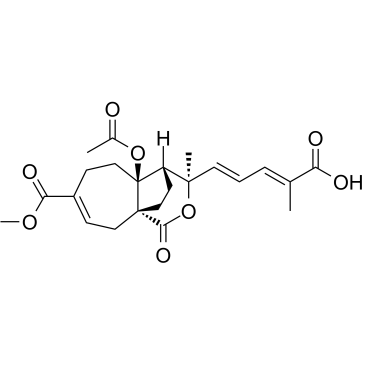
Pseudolaric acid B structure
|
Common Name | Pseudolaric acid B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82508-31-4 | Molecular Weight | 432.464 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 613.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H28O8 | Melting Point | 166°C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 208.8±25.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Pseudolaric acid BPseudolaric Acid B is a diterpene isolated from the root of Pseudolarix kaempferi Gorden (pinaceae), has anti-cancer, antifungal, and antifertile activities, and shows immunosuppressive activity on T lymphocytes[1][2][3]. Pseudolaric Acid B inhibits hepatitis B virus (HBV) secretion through apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Pseudolaric Acid B induces autophagy[4][5]. |
| Name | pseudolaric acid b |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pseudolaric Acid B is a diterpene isolated from the root of Pseudolarix kaempferi Gorden (pinaceae), has anti-cancer, antifungal, and antifertile activities, and shows immunosuppressive activity on T lymphocytes[1][2][3]. Pseudolaric Acid B inhibits hepatitis B virus (HBV) secretion through apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Pseudolaric Acid B induces autophagy[4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 613.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 166°C |
| Molecular Formula | C23H28O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 432.464 |
| Flash Point | 208.8±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 432.178406 |
| PSA | 116.20000 |
| LogP | 2.78 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.565 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: soluble1mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P281-P301 + P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | 25-62 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37-45-24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
|
~62% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Trost, Barry M.; Waser, Jerome; Meyer, Arndt Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008 , vol. 130, # 48 p. 16424 - 16434 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
~% 
Pseudolaric acid B CAS#:82508-31-4 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 43, # 22 p. 4095 - 4098 |
|
Newly discovered angiogenesis inhibitors and their mechanisms of action.
Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 33(9) , 1103-11, (2012) In the past decade, the success of angiogenesis inhibitors in clinical contexts has established the antiangiogenic strategy as an important part of cancer therapy. During that time period, we have dis... |
|
|
Bcl-2 family proteins were involved in pseudolaric acid B-induced autophagy in murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells.
J. Pharmacol. Sci. 107(3) , 295-302, (2008) Pseudolaric acid B (PAB) exerted cytostatic activity on murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells. The cytostatic mechanism of PAB on L929 cells was investigated in this paper. At 36 h, after 80 microM PAB treat... |
|
|
In vitro synergy of pseudolaric acid B and fluconazole against clinical isolates of Candida albicans.
Mycoses 54(5) , e400-6, (2011) Candida albicans is the most common fungal pathogen in humans. The emergence of resistance to azole antifungals has raised the issue of using such antifungals in combination to optimise therapeutic ou... |
| (2E,4E)-5-[(1R,7S,8R,9R)-4,7-Bis(methoxycarbonyl)-9-methyl-11-oxo-10-oxatricyclo[6.3.2.0]tridec-3-en-9-yl]-2-methylpenta-2,4-dienoic acid |
| (2E,4E)-5-[(1S,7S,8S,9R)-7-Acetoxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-9-methyl-11-oxo-10-oxatricyclo[6.3.2.0]tridec-3-en-9-yl]-2-methyl-2,4-pentadienoic acid |
| 1H-4,9a-Ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylic acid, 4a-(acetyloxy)-3-[(1E,3E)-4-carboxy-1,3-pentadien-1-yl]-3,4,4a,5,6,9-hexahydro-3-methyl-1-oxo-, 7-methyl ester, (3R,4S,4aS,9aS)- |
| (2E,4E)-5-[(1R,7S,8R,9R)-4,7-Bis(methoxycarbonyl)-9-methyl-11-oxo-10-oxatricyclo[6.3.2.0]tridec-3-en-9-yl]-2-methyl-2,4-pentadienoic acid |
| 1H-4,9a-Ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-4a,7(5H)-dicarboxylic acid, 3-[(1E,3E)-4-carboxy-1,3-pentadien-1-yl]-3,4,6,9-tetrahydro-3-methyl-1-oxo-, 4a,7-dimethyl ester, (3R,4R,4aS,9aR)- |
| PLAB |
| (2E,4E)-5-[(1S,7S,8S,9R)-7-Acetoxy-4-(methoxycarbonyl)-9-methyl-11-oxo-10-oxatricyclo[6.3.2.0]tridec-3-en-9-yl]-2-methylpenta-2,4-dienoic acid |
| PseudolaricAcidB |
| Pseudolarix acid B |
![(1R,7S,8S,9S)-7-acetoxy-9-ethynyl-9-methyl-11-oxo-10-oxa-tricyclo[6.3.2.01,7]tridec-3-ene-4-carboxylic acid methyl ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/485/1000669-90-8.png)
![methyl (3R,4R,4aS,9aR)-4a-hydroxy-3-((1E,3E)-5-hydroxy-4-methylpenta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-oxo-3,4,4a,5,6,9-hexahydro-1H-4,9a-ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/491/457622-28-5.png)

![methyl (3S,4R,4aS,7S,9aR)-3-formyl-4a-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxooctahydro-1H-4,9a-ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/029/457622-27-4.png)
![methyl (3S,4R,4aS,7S,9aR)-4a-acetoxy-3-formyl-3-methyl-1-oxooctahydro-1H-4,9a-ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/474/457622-33-2.png)
![methyl (3R,4R,4aS,7S,9aR)-4a-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-oxo-3-((E)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)octahydro-1H-4,9a-ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/098/457622-30-9.png)
![methyl (3R,4R,4aS,7S,9aR)-4a-hydroxy-3-((E)-3-hydroxyprop-1-en-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-oxooctahydro-1H-4,9a-ethanocyclohepta[c]pyran-7-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/050/457622-31-0.png)

