Hydroxypropyl Cellulose
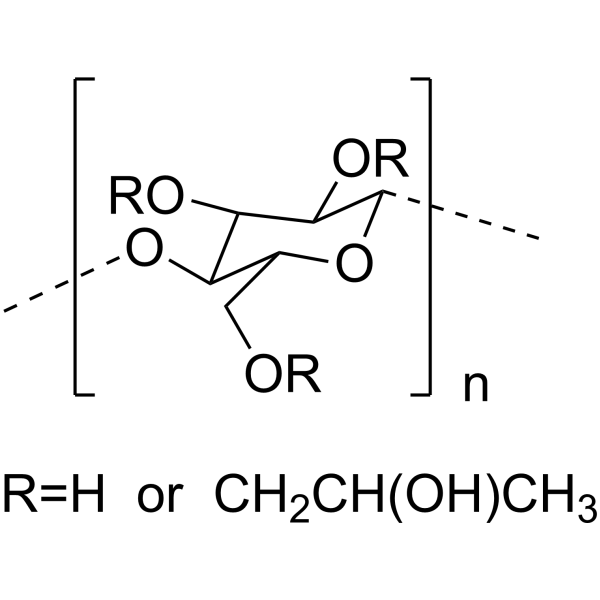
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose structure
|
Common Name | Hydroxypropyl Cellulose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9004-64-2 | Molecular Weight | 806.930 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 891.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H70O19 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 492.8±34.3 °C | |
Use of Hydroxypropyl CelluloseHydroxypropyl Cellulose is somewhat amphiphilic in character and is a surfactant. Hydroxypropyl Cellulose can be used as a pharmaceutical excipient, such as coating agent, emulsifier, suspension, tablet, thickener, viscosifier. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1][2]. |
| Name | Hydroxypropyl cellulose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hydroxypropyl Cellulose is somewhat amphiphilic in character and is a surfactant. Hydroxypropyl Cellulose can be used as a pharmaceutical excipient, such as coating agent, emulsifier, suspension, tablet, thickener, viscosifier. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 891.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C36H70O19 |
| Molecular Weight | 806.930 |
| Flash Point | 492.8±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 806.451111 |
| LogP | -1.24 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | White to light cream |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.532 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Combustible. |
| Water Solubility | polar oganic solvents: soluble |
|
Polymer-directed crystallization of atorvastatin.
J. Pharm. Sci. 101(8) , 2941-51, (2012) Living organisms secrete minerals composed of peptides and proteins, resulting in "mesocrystals" of three-dimensional-assembled composite structures. Recently, this biomimetic polymer-directed crystal... |
|
|
Stabilization of fenofibrate in low molecular weight hydroxypropylcellulose matrices produced by hot-melt extrusion.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 39(2) , 290-8, (2013) The objective of this study was to improve the dissolution rate and to enhance the stability of a poorly water-soluble and low glass-trasition temperature (T(g)) model drug, fenofibrate, in low molecu... |
|
|
Improved supersaturation and oral absorption of dutasteride by amorphous solid dispersions.
Chem. Pharm. Bull. 60(11) , 1468-73, (2012) In this study, amorphous solid dispersions containing dutasteride and various excipients, manufactured by spray-drying processes, were characterized to determine the effects on their ability to form s... |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, 2-hydroxypropyl 2,3,6-tris-O-(2-hydroxypropyl)-4-O-[2,3,4,6-tetrakis-O-(2-hydroxypropyl)-α-D-glucopyranosyl]- |
| Klucel |
| MFCD00132688 |
| 2-Hydroxypropyl 2,3,6-tris-O-(2-hydroxypropyl)-4-O-[2,3,4,6-tetrakis-O-(2-hydroxypropyl)-α-D-glucopyranosyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside |

