Bromfenac Sodium
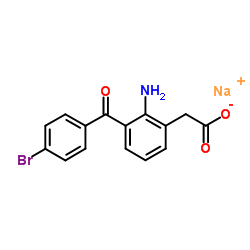
Bromfenac Sodium structure
|
Common Name | Bromfenac Sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91714-93-1 | Molecular Weight | 356.147 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 562.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H11BrNNaO3 | Melting Point | 285ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 293.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Bromfenac SodiumBromfenac sodium is a potent and orally active inhibitor of COX, with IC50s of 5.56 and 7.45 nM for COX-1 and COX-2, respectively. Bromfenac sodium is a brominated non-steroidal anti-inflammatory/analgesic drug (NSAID), and it is commonly used for the research of postoperative inflammation and pain following cataract surgery, and pseudophakic cystoid macular edema (CME)[1][2]. |
| Name | bromfenac sodium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bromfenac sodium is a potent and orally active inhibitor of COX, with IC50s of 5.56 and 7.45 nM for COX-1 and COX-2, respectively. Bromfenac sodium is a brominated non-steroidal anti-inflammatory/analgesic drug (NSAID), and it is commonly used for the research of postoperative inflammation and pain following cataract surgery, and pseudophakic cystoid macular edema (CME)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
COX-1:5.56 nM (IC50) COX-2:7.45 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Bromfenac (90 μg/mL; 48 h) inhibits TGF-b1-induced extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis and myofibroblast activation in HConFs and HPFs[3]. Bromfenac (30-90 μg/mL; 48 h) decreases the protein and mRNA expression levels of FN, COL3, a-SMA, and survivin in a dose-dependent manner in HConFs and HPFs[3]. Bromfenac (30-90 μg/mL; 48 h) declines the phosphorylated protein levels of AKT, ERK1/2, and GSK-3b-S9 with dosage in HPFs and HConFs[3]. |
| In Vivo | Bromfenac (0.0032-3.16%; 100 or 200 μL; rubbed onto the backs) produces significant anti-inflammatory activity at concentrations as low as 0.1% (4 h pretreatment time) or 0.32% (18h pretreatment time) in rats[2]. Bromfenac (0.032-3.16%; 100 μL; rubbed onto the paws) produces dose-related anti-inflammatory activity in rats[2]. Bromfenac (0.032-1.0%; 50 μL) is 26 times more potent than indomethacin in blocking the erythema when applied directly onto the skin area exposed to UV light in guinea pigs[2]. Bromfenac (0.0032-0.1%; 50μL; rubbed onto the uninjected paw for 4 h per day and 5 days per week) produces a dose and time dependent reduction in the paw volume of both hind limbs in rats[2]. Bromfenac (0.32%; 50μL; rubbed onto the abdomen) produces significant blockade of abdominal constriction to ACh challenge in mice[2]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (150-250 g) are injected carrageenan[2] Dosage: 0.0032, 0.01, 0.032, 0.1, 0.32, 1.0, 3.16% (100 or 200 μL) Administration: Rubbed onto the backs before 1-72 h of injected carrageenan Result: Produced significant anti-inflammatory activity when applied 1, 2, and 4 h prior to carrageenan challenge at 0.32%. Applied 1 or 4 h prior to carrageenan challenge was active, but not when applied 24 h (or longer) prior to challenge at 0.2%. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 562.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 285ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H11BrNNaO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 356.147 |
| Flash Point | 293.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 354.981995 |
| PSA | 83.22000 |
| LogP | 2.13590 |
| Appearance of Characters | faint yellow to dark yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.77E-13mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: ≥5mg/mL |
|
~55% 
Bromfenac Sodium CAS#:91714-93-1 |
| Literature: Walsh; Moran; Shamblee; Uwaydah; Welstead Jr.; Sancilio; Dannenburg Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1984 , vol. 27, # 11 p. 1379 - 1388 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Multiparametric assay using HepaRG cells for predicting drug-induced liver injury.
Toxicol. Lett. 236 , 16-24, (2015) The utility of HepaRG cells as an in vitro cell-based assay system for assessing drug-induced liver injury (DILI) risk was investigated. Seventeen DILI-positive and 15 DILI-negative drugs were selecte... |
|
|
Efficacy of ophthalmic nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in suppressing anterior capsule contraction and secondary posterior capsule opacification.
J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 35(9) , 1614-8, (2009) To evaluate the efficacy of ophthalmic nonsteroidal and steroidal antiinflammatory drugs in preventing anterior capsule contraction and secondary posterior capsule opacification (PCO) using an experim... |
|
|
Cyclooxygenase (COX)-inhibiting drug reduces HSV-1 reactivation in the mouse eye model.
Curr. Eye Res. 34(3) , 171-6, (2009) To examine the effects of COX inhibitors on suppressing HSV-1 reactivation in a mouse model.BALB/c mice were latently infected with HSV-1 and treated by 0.1% bromfenac Na eye drops, 0.1% pranoprofen e... |
| Bromfenacsodium |
| BENZENEACETIC ACID, 2-AMINO-3-(4-BROMOBENZOYL)-, MONOSODIUM SALT |
| BENZENEACETIC ACID,2-AMINO-3-(4-BROMOBENZOYL)-, SODIUM SALT (1:1) |
| bromfenac sodium salt |
| {2-amino-3-[(4-bromophényl)carbonyl]phényl}acétate de sodium |
| sodium {2-amino-3-[(4-bromophenyl)carbonyl]phenyl}acetate |
| Sodium [2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl)phenyl]acetate |
| Natrium-{2-amino-3-[(4-bromphenyl)carbonyl]phenyl}acetat |
| Bronuck |
| Benzeneacetic acid, 2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl)-, sodium salt (1:1) |
| Bromfenac sodium |
