Azacitidine (5-Azacytidine)
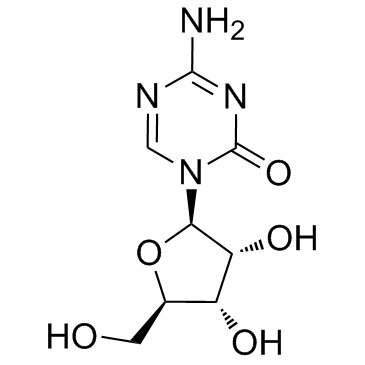
Azacitidine (5-Azacytidine) structure
|
Common Name | Azacitidine (5-Azacytidine) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 320-67-2 | Molecular Weight | 244.205 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 534.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N4O5 | Melting Point | 226-232 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 277.0±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
The high mobility group A2 protein epigenetically silences the Cdh1 gene during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43(1) , 162-78, (2015) The loss of the tumour suppressor E-cadherin (Cdh1) is a key event during tumourigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) triggers EMT by inducing the expression of non-histone chromatin protein High Mobility Gr... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Vibrio vulnificus VvpE inhibits mucin 2 expression by hypermethylation via lipid raft-mediated ROS signaling in intestinal epithelial cells.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1787, (2015) Mucin is an important physical barrier against enteric pathogens. VvpE is an elastase encoded by Gram-negative bacterium Vibrio vulnificus; however, the functional role of VvpE in intestinal mucin (Muc) production is yet to be elucidated. The recombinant prot... |
|
|
Curcumin and dimethoxycurcumin induced epigenetic changes in leukemia cells.
Pharm. Res. 32(3) , 863-75, (2015) Curcumin is an ideal chemopreventive and antitumor agent characterized by poor bioavailability and low stability. The development of synthetic structural analogues like dimethoxycurcumin (DMC) could overcome these drawbacks. In this study we compared the cyto... |
|
|
Epigenetic regulation of microRNA expression in renal cell carcinoma
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 436(1) , 79-84, (2013) • microRNAs are silenced by histone acetylation. • 5-Aza-2′dC and SAHA induce microRNA re-expression. • 5-Aza-2′dC and SAHA are most efficient in combination. |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |