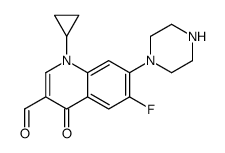
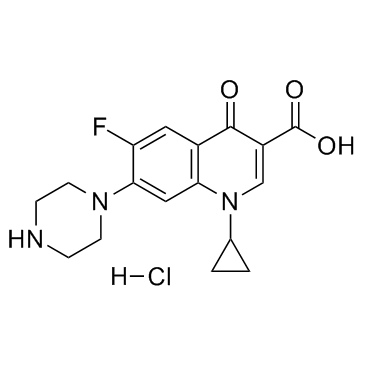
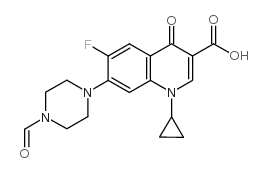
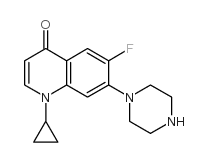
85721-33-1
| Name | ciprofloxacin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CPFX
ciproiv CIPROBAY euciprin Cipro Ciprine ciloxan Ciprofloxacin Cipmbay ciprobid Baycip MFCD00185755 |
| Description | Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, exhibiting potent antibacterial activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, exhibiting potent antibacterial activity[1]. Ciprofloxacin (CIP) shows potent activity against Y. pestis with MIC90 of 0.03 μg/mL[2]. |
| In Vivo | Ciprofloxacin (1 mg/L) induces glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity, in contrast with inhibited GST and Catalase (CAT) of larvae exposed to enrofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin (≥10 μg/L) and enrofloxacin are ecotoxic for development, growth, detoxifying, and oxidative stress enzymes in anuran amphibian larvae[1]. In a murine model of pneumonic plague, Ciprofloxacin (30 mg/kg, i.p.) results in a drug exposure which is similar to the drug exposure observed in human following a 500 mg dose of oral Ciprofloxacin. Intraperitoneal Ciprofloxacin reduces the lung bacterial load compare to controls treated with intraperitoneal PBS[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Bacterial inocula are prepared by suspending colonies into Mueller-Hinton broth (CAMHB) (containing Ciprofloxacin) from 18 to 24 h (B. anthracis) or 42 to 48 h (Y. pestis) on sheep blood agar (SBA) plates that are incubated at 35°C. Suspended cultures are diluted with CAMHB to a bacterial cell density of 105 CFU/mL adjusted based on the optical density at 600 nm. To each well of the 96-well plate, 50 μL of dilutions is added for a final inoculum of ~5×104 CFU/well. Plates are incubated at 35°C. MICs are determined visually at 18 to 24 h (B. anthracis) or 42 to 48 h (Y. pestis) and also by absorbance at 600 nm[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Female BALB/cAnNCrl (BALB/c) mice, 8 to 10 weeks old and 20 g (±4 g) are used in this assay. A single dose of Ciprofloxacin (30 mg/kg) is administered to mice (n=30) via the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route. The mice (n=3/time point/group) are culled at 1, 10, 20, or 30 min and 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 8, 12 h following Ciprofloxacin administration and 1, 15, or 30 min and 1, 2, 4, 6, 10, 18, or 24 h following DRCFI or CFI administration. Blood sampling points are chosen based upon the short half-life of Ciprofloxacin and longer half-life of CFI. Blood and lungs (whole organ) are collected post mortem for analysis. The lung doses following CFI or DRCFI administration are calculated using the concentration of Ciprofloxacin in the lung samples at 1 min post-administration[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 581.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 255-257°C |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 331.341 |
| Flash Point | 305.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 331.133209 |
| PSA | 74.57000 |
| LogP | 0.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 |
| Storage condition | Store at 0-5°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | VB1993800 |
| HS Code | 3004909090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 3004909090 |
|---|

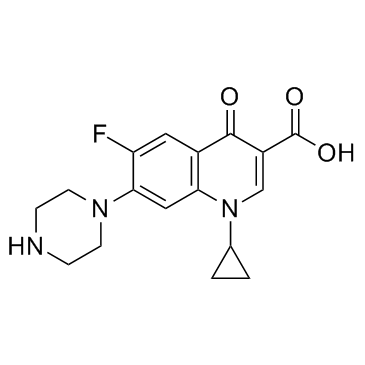

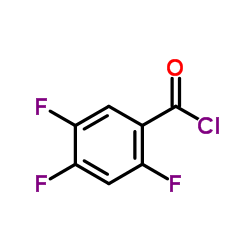
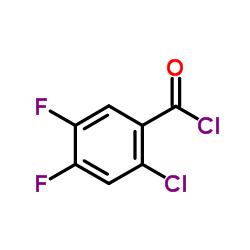
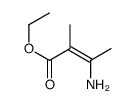
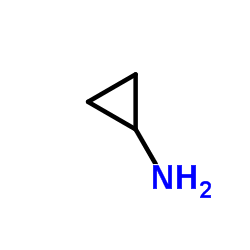
![3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-7-[4-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1-piperazinyl]-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/288/93594-29-7.png)