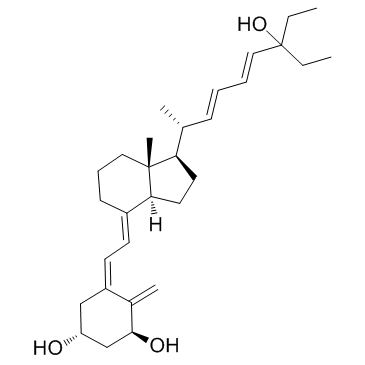
134404-52-7
| Name | EB 1089,(1R,3S,5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,2E,4E)-6-Ethyl-6-hydroxy-1-methyl-2,4-octadien-1-yl]-octahydro-7α-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylene-1,3-cyclohexanediol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(1R,3S,5E)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R,3E,5E)-7-ethyl-7-hydroxynona-3,5-dien-2-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol (non-preferred name)
(1R,3S,5E)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R,3E,5E)-7-Ethyl-7-hydroxy-3,5-nonadien-2-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]-4-methylene-1,3-cyclohexanediol 1,3-Cyclohexanediol, 5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(1R,2E,4E)-6-ethyl-6-hydroxy-1-methyl-2,4-octadien-1-yl]octahydro-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylene-, (1R,3S,5E)- (1R,3S,5E)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R,3E,5E)-7-Ethyl-7-hydroxynona-3,5-dien-2-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]-4-methylenecyclohexane-1,3-diol (non-preferred name) (1R-(1a(1R*,2E,4E),3ab,4E(1R*,3S*,5Z),7aa))-5-((1-(6-Ethyl-6-hydroxy-1-methyl-2,4-octadienyl)octahydro-7a-methyl-4H-inden-4-ylidene)ethylidene)-4-methylene-1,3-cyclohexanediol Seocalcitol (1R,3S,5E)-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(2R,3E,5E)-7-Ethyl-7-hydroxynona-3,5-dien-2-yl]-7a-methyloctahydro-4H-inden-4-yliden}ethyliden]-4-methylencyclohexan-1,3-diol (non-preferred name) 1(S),3(R)-dihydroxy-20(R)-(5'-ethyl-5'-hydroxyhepta-1'(E),3'(E)-dien-1'-yl)-9,10-secopregna-5(Z),7(E),10(19)-triene |
| Description | Seocalcitol is a vitamin D analog, binds vitamin D receptor protein from human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells with Kd of 0.27 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 0.27 nM (vitamin D receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Seocalcitol (EB 1089) is a stimulators of osteoclast recruitment in murine bone marrow cultures, with EC50 at 0.1 nM. Seocalcitol stimulates bone resorption with an estimated EC50 at 0.03 nM[1]. Seocalcitol (EB 1089) elicites a dose-dependent induction of 24-hydroxylase mRNA in the kidney (EC50=0.4±0.13). In the kidney, Kd values for Seocalcitol is 0.48±0.04 nM. However, in the intestine, the Kd for Seocalcitol is 1.43±0.19 nM)[2]. Seocalcitol (0.1-10 nM) induces cell differentiation in a dosedependent manner. A higher differentiating activity is observed for 1 nM Seocalcitol (EB 1089) than for 1 nM VD3. |
| In Vivo | Seocalcitol (EB1089), a synthetic vitamin D analog, exhibits reduced hypercalcemic activity relative to 1,25(OH)2VD3. In another study, long-term intraperitoneal (IP) administration of Seocalcitol at a dose of 0.5 μg/kg body weight every other day in C3H/Sy mice exertes a very strong inhibitory effect on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development[4]. Seocalcitol (EB 1089) is administered daily to postnatal rats from 4 to 12 days of age (P4 to P12) by intraperitoneal injection at either 0.38 or 1.25 μg/kg body weight (BW)/day. Only the highest dose of Seocalcitol (1.25 μg/kg BW) causes a significant reduction in weight gain when administered alone or in conjunction with Dexamethasone, all-trans retinoic acid (RA), or retinoic acid[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | Vitamin D receptor protein is prepared from cultures of human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63. Suspensions of 5×107 cells/mL are homogenized, sonicated, and centrifuged at 30,000g for 1 h at 4°C. The presence of the 1α,25(OH)2D3 receptor is verified by sucrose density gradient analysis. The supernatants are adjusted to 2 mg protein/mL and used for binding studies. Samples of 500 μL are incubated with 10,000 dpm [3H]1α,25(OH)2D3 (180 Ci/mmol) and increasing concentrations of 1α,25(OH)2D3 or vitamin D3 analogs are added. After incubation for 60 min at 22°C, bound and free [3H]1α,25(OH)2D3 are separated on dextran-coated charcoal. Each compound is tested in three separate experiments[1]. |
| Cell Assay | This fluorescent dye allowed to determine ROS release in HL60 cells, untreated or treated VD3 or Seocalcitol. Briefly, after treatment, HL60 cells are washed and re-suspended at 106 cells/mL in RPMI-1640 without FCS and phenol red. Then, 10 μM H2-DCFDA probe is added to each plate at a final volume of 2 mL. Cells are incubated for 45 min at 37°C in the dark. A second wash is made before the fluorescence analysis using spectrometer at 488 nm intensity excitation λex and 516 nm emission λem. Results, in arbitrary fluorescence units (AFU), are expressed according to the ratio [(AFU-treated cells)/(AFU control cells)]×100[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Six- to eight-week-old male BALB/c NU/Nu mice are inoculated subcutaneously with 106 SKHEP-1 cells into the right flank. Twenty-four hours after inoculation, mice are randomly assigned to a control group (n=10) or the treatment groups (n=10), receiving 0.02, 0.1 or 0.5 μg/kg per day of Seocalcitol (intraperitoneal or oral on alternate days). Control animals receive propylene glycol alone. Tumor size is measured using vernier calipers every third day and the volumes are estimated using the formula 0.5×length×(width)2. Animals receive sterile food and water. Rats[5] Newborn Sprague-Dawley rat pups are randomly assigned to 1 of 6 treatment groups, consisting of daily intraperitoneal injections of the vitamin D analogue Seocalcitol (0.38 or 1.25 μg/kg body weight) alone, or in combination with all-trans retinoic acid (RA; 500 μg/kg body weight) and/or Dexamethasone (DEX; 0.25 μg/day) in a 3×2×2 factorial design. Seocalcitol and RA injections are conducted on P3 through P12, whereas Dexamethasone is administered on P4 through P12. Seocalcitol is prepared for injections in a quantity sufficient for all injections by dilution from a stock solution (4 mM in isopropanol) into the carrier Solutol HS 15 (BASF). Solutol-diluted Seocalcitol is stored as aliquots in sealed glass vials under nitrogen gas at 4°C, with daily injections conducted with freshly unsealed aliquots of Seocalcitol. Stock solutions of RA (50 mg/mL DMSO are stored under nitrogen at −80°C and prepared for injection by dilution of freshly thawed aliquots into cottonseed oil (2 μg/μL). A Dexamethasone stock solution (10 mg/mL ethanol) is stored under nitrogen at 4°C and prepared fresh for daily injections in 0.9% NaCl (0.25 μg/μL). All rats receive equivalent volumes of the 3 carrier solutions employed (solutol, cottonseed oil, 0.9% NaCl). Seocalcitol and RA are administered as a 2-phase solution via a 10 μL injection using a 20 μL glass-barreled syringe and a 28-gauge needle, whereas Dexamethasone is administered in a separate 10 μL injection. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 608.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H46O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 454.684 |
| Flash Point | 252.3±26.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 454.344696 |
| PSA | 60.69000 |
| LogP | 7.02 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.560 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |