2095432-58-7
| Name | SAG hydrochloride |
|---|
| Description | SAG (hydrochloride) is a potent Smo receptor agonist, and activates the Hedgehog signaling pathway, with a Kd of 59 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 59 nM (Smo)[1]. |
| In Vitro | SAG (hydrochloride) acts downstream of Ptch1 in the Hh pathway and counteracts cyclopamine inhibition of Smo. SAG induces firefly luciferase expression in Shh-LIGHT2 cells with an EC50 of 3 nM and then inhibits expression at higher concentrations. In Smo-expressing Cos-1 cells, SAG yields an apparent dissociation constant (KD) of 59 nM for the SAG/Smo complex[1]. SAG and purmorphamine verride the inhibitory effect of robotnikinin since Smo functions downstream of Shh/Ptc1[2]. |
| In Vivo | In CD-1 mice, SAG (1.0 mM) or NELL-1 (600 μg/ml) alone results in increased bone formation at 4 and 8 weeks, but significantly greater bone formation with both components combined (SAG + NELL-1). The combination of the two compounds exhibits a significant increase in new bone formation, accompanied by increased defect vascularization[3]. SAG (15, 17, or 20 mg/kg, i.p.) induces pre-axial polydactyly prevalently. The highest SAG dose is effective in ca. 80% of the embryos and increased Gli1 and Gli2 mRNA expression in the limb bud, with Gli1 mRNA being the most upregulated[4]. |
| References |
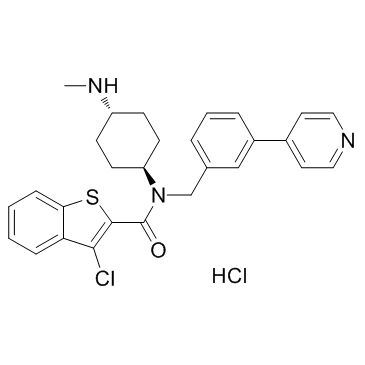
| Molecular Formula | C28H29Cl2N3OS |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 526.52 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |