22427-39-0
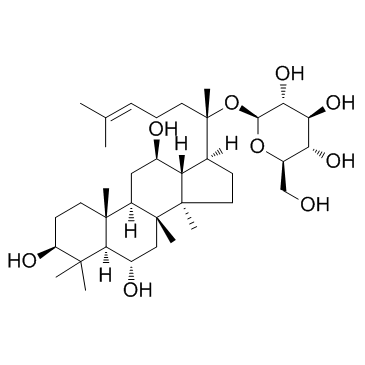
| Name | ginsenoside Rg1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-({(3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-3,12-Dihydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentaméthyl-17-[(2S)-6-méthyl-2-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-5-heptèn-2-yl]hexadécahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phénanthrén-6-yl}oxy)-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol
GINSENOSIDE RGL PANAXOSIDE A Ginsenoside Rg1 EINECS 244-989-9 MFCD00210293 ginsenoside-Rg2 (3β,6α,12β)-20-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3,12-dihydroxydammar-24-en-6-yl β-D-glucopyranoside panaxosiderg1 (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-({(3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-3,12-Dihydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-[(2S)-6-methyl-2-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-5-hepten-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-6-yl}oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol (3β,6α,12β)-20-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3,12-dihydroxydammar-24-en-6-yl-β-D-glucopyranoside Gensenoside Rg1 ginsenosidea2 GinsenosideRg1 Rg1 β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,6α,12β)-20-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3,12-dihydroxydammar-24-en-6-yl SANCHINOSIDE C1 ginsenosideg1 ginsinoside Rg1 |
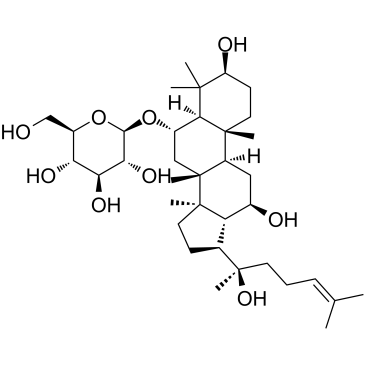
| Description | Ginsenoside Rg1 is one of the major active components of ginseng. Ginsenoside Rg1 displays promising effects by reducing cerebral Aβ levels. Ginsenoside Rg1 also reduces NF-κB nuclear translocation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Aβ1-42 p65 |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes the proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). The proliferative ability of hDPCs in Ginsenoside Rg1 is significantly enhanced (p<0.05), especially in the Ginsenoside Rg1 (5 μM) group. ALP activity and gene expressions of DSPP and DMP1 are increased in the induction group, Ginsenoside Rg1 group, and their combination group compared with the control group (p<0.05)[3]. In the RAW264.7 cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) , the level of p-IκBα and p-p65 is significantly higher than in controls and PPAR-γ levels are significantly lower. Treatment with Rg1 vitro inhibits IκBα phosphorylation, reduces NF-κB nuclear translocation and upregulates PPAR-γ expression[2]. |
| In Vivo | In the inflamed joints of adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rats, the level of p-IκBα and p-p65 is significantly higher than in controls and PPAR-γ levels are significantly lower. Treatment with Ginsenoside Rg1 in vivo inhibits IκBα phosphorylation, reduces NF-κB nuclear translocation and upregulates PPAR-γ expression[2]. Ginsenoside Rg1 (G-Rg1) and Ginsenoside Rg2 (G-Rg2) reduce the escape latencies on the last two training days compared to the Alzheimer's disease (AD) model group (p<0.05). In the spatial exploration test, the total time spent in the target quadrant and the number of mice that exactly crossed the previous position of the platform are clearly shorter and lower, respectively, in the AD model group mice than in the normal control group mice (p<0.01), a trend that is reversed by treatment with Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 (Ginsenoside Rg1, p<0.01; Ginsenoside Rg2, p<0.05). Treatment with Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 effectively improve cognitive function of the mice that have declined due to AD. Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 reduce Aβ1-42 accumulation in APP/PS1 mice. In the Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 treated mice, the pathological abnormalities observed in the APP/PS1 mice are gradually ameliorated. Clear nucleoli and light brown, sparsely scattered Aβ deposits are visible[1]. |
| Cell Assay | hDPCs are incubated with different concentrations of Ginsenoside Rg1 (0.1, 0.5, 2.5, 5, 10 and 20 μM) . The effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the proliferative ability of hDPCs are evaluated by a fibroblast colony forming test, MTT assay and flow cytometry for cell cycle. The control group, osteogenic induction group, Ginsenoside Rg1 (5 μM) group and combination group are designed, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and FQ-PCR for gene expressions of dentine sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) and dentine matrix protein 1 (DMP1) are performed to evaluate the differentiation of hDPCs[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Male APP/PS1 mice, weighing 20±2 g, and male C57BL/6J mice, weighing 20±2 g, are used. The animals are maintained in an air-conditioned animal center at 23±2°C and a relative humidity of 50±10%, with a natural light-dark cycle. Food and water are available ad libitum. After acclimatization for 1 wk, the mice are divided into four groups (n=10 in each group): the normal control group, the AD model group, the Ginsenoside Rg1 group, and the Ginsenoside Rg2 group. According to the concentration-response curves, the mice in the Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 groups are injected intraperitoneally once daily with Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rg2 (30 mg/kg), respectively, dissolved in saline. The mice in the AD model group (APP/PS1 mice) and the normal control group (C57BL/6J nontransgenic littermates) are treated with isodose saline (0.9% w/v). All mice are treated for 1 mo before brain metabolite profiling. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 898.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 194~197 ℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C42H72O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 801.013 |
| Flash Point | 497.2±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 800.492188 |
| PSA | 239.22000 |
| LogP | 1.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.602 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 2-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1230 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3.0 |
| RTECS | LY9537200 |
|
~% 
22427-39-0 |
| Literature: EP2570132 A2, ; Paragraph 0049; 0050; 0051 ; |
|
~% 
22427-39-0 |
| Literature: Zou, Kun; Zhu, Shu; Tohda, Chihiro; Cai, Shaoqing; Komatsu, Katsuko Journal of Natural Products, 2002 , vol. 65, # 3 p. 346 - 351 |
|
~% 
22427-39-0 |
| Literature: Planta Medica, , vol. 69, # 3 p. 285 - 286 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |