53963-43-2
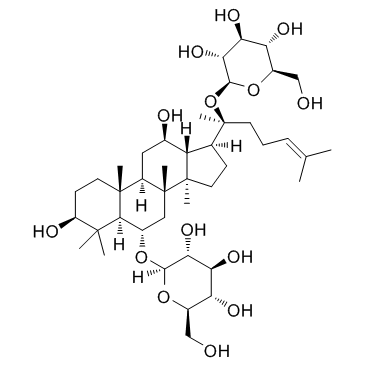
| Name | ginsenoside F1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,6α,12β)-3,6,12-trihydroxydammar-24-en-20-yl
Ginsenoside F1 GINSENOSIDEF1 Ginsenoside-F1 (3β,6α,12β)-3,6,12-Trihydroxydammar-24-en-20-yl β-D-glucopyranoside |
| Description | Ginsenoside F1, an enzymatically modified derivative of Ginsenoside Rg1, demonstrates competitive inhibition of CYP3A4 activity and weaker inhibition of CYP2D6 activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CYP3A4 |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside F1 has been shown to flaunt anticancer, anti-aging, and antioxidant effects and has demonstrated competitive inhibition of CYP3A4 activity and weaker inhibition of CYP2D6 activity. The cell viabilities are 68% at the highest concentration of ginsenoside F1 (200μM) in MTT assays[1]. |
| In Vivo | ApoE-/- mice are fed a high fat diet and orally treated with Ginsenoside F1 (50 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks. Ginsenoside F1 treated mice significantly reduce the lesion size compared with model group mice[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | Glycosylation ability is assayed with overexpressed BSGT1 enzyme and F1. The reaction mixtures contain 100 μL of 0.5 mM F1 and 100 μL of 2.5 mM UDP-glucose and 800 μL of purified enzyme (final concentration at 0.1 mg/mL) (pH 7.0). The mixtures are incubated at 30°C for 24 h. Moreover, three groups of controls are incubated under the same conditions: (1) control 1 (C1) consists of Ginsenoside F1 with BSGT1; (2) control 2 (C2) consists of BSGT1 with UDP-glucose; and (3) control 3 (C3) consists of Ginsenoside F1 with UDP-glucose[1]. |
| Cell Assay | B16BL6 cells are cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagles medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified 95% air/5% CO2 atmosphere. Cell viability is determined for Ginsenoside F1 and metabolite 1 using MTT conversion to formazan. Cells are seeded at a density of 1×105 cells/well in a 96-well plate, cultured for 24 h, and treated with various concentrations from 1 μM to 200 μM of Ginsenoside F1 and metabolite 1 for 5 d. Finally, 10 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL in PBS) is added to each well. Cells are incubated at 37°C for 3 h, and then DMSO (100 μL) is added to dissolve the formazan crystals. The absorbance is measured at 570 nm with the reference wavelength of 630 nm using an ELISA reader[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Six-week-old (17±1 g) male C57BL/6 mice and ApoE-/- mice with a C57BL/6 background are maintained in a temperature-controlled facility (temperature: 22±1°C; humidity: 60%) with a 14 h light/10 h dark cycle in conventional cages. Forty mice are randomly divided into four experimental groups (n=10/group): (I) C57BL/6 N mice, the control group; (II) ApoE-/- mice group; (III) ApoE-/- mice+ Ginsenoside F1 group; (IV) ApoE-/- mice+Probucol group. All mice are fed with a high fat diet (HFD, 0.3% cholesterol and 20% pork fat) for 8 weeks. Ginsenoside F1 (50 mg/kg/day, i.g.) and Probucol (2 g/kg, i.g.) are dissolved in carboxymethyl cellulose sodium (CMC-Na). Oral administration is given to mice every day for 8 weeks. The control and model groups receive the aseptic 0.5% CMC-Na treatment every day (i.g., 0.1 mL/10g) [2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 751.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C36H62O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 638.872 |
| Flash Point | 408.4±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 638.439392 |
| PSA | 160.07000 |
| LogP | 3.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.581 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~22% 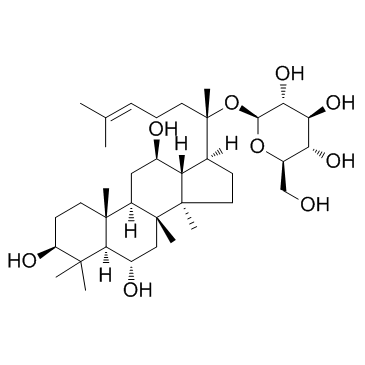
53963-43-2 |
| Literature: Danieli; Luisetti; Riva; Bertinotti; Ragg; Scaglioni; Bombardelli Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1995 , vol. 60, # 12 p. 3637 - 3642 |
|
~% 
53963-43-2 |
| Literature: Planta Medica, , vol. 69, # 3 p. 285 - 286 |
|
~% 
53963-43-2 |
| Literature: Planta Medica, , vol. 69, # 3 p. 285 - 286 |
|
~% 
53963-43-2 |
| Literature: Planta Medica, , vol. 69, # 3 p. 285 - 286 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |