119188-33-9
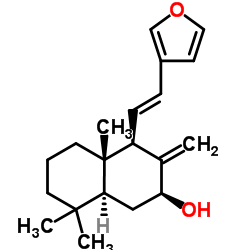
| Name | (2S,4R,4aS,8aS)-4-[(E)-2-(3-Furyl)vinyl]-4a,8,8-trimethyl-3-methy lenedecahydro-2-naphthalenol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(2S,4R,4aS,8aS)-4-[(E)-2-(furan-3-yl)ethenyl]-4a,8,8-trimethyl-3-methylidenedecahydronaphthalen-2-ol
2-Naphthalenol, 4-[(E)-2-(3-furanyl)ethenyl]decahydro-4a,8,8-trimethyl-3-methylene-, (2S,4R,4aS,8aS)- (2S,4R,4aS,8aS)-4-[(E)-2-(3-Furyl)vinyl]-4a,8,8-trimethyl-3-methylenedecahydro-2-naphthalenol |
| Description | Coronarin A is an orally active natural compound that inhibits mTORC1 and S6K1 to increase IRS1 activity. Coronarin A shows anti-inflammatory activity and can also be used for type 2 diabetes mellitus research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mTORC1 S6K1 |
| In Vitro | Coronarin A (3-30 μM; 4 or 12 h) stimulates glycogen synthesis through activating PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling and inhibits gluconeogenesis by activating ERK-dependent Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 pathway in rat primary hepatocytes[1]. Coronarin A (1-30 μM; 4 h) increases tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 through inhibiting mTOR/S6K1 signaling[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Primary rat hepatocytes Concentration: 1, 3, 10 and 30 μM Incubation Time: 4 h Result: Increased the Akt and GSK3β phosphorylation dose-dependently. Dose-dependently stimulated the phosphorylation of both ERK1 and ERK2. Increased the phosphorylation of β-catenin and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK). Dose-dependently enhanced the tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 at Tyr1222, whereas the serine phosphorylation of IRS1 was dose-dependently inhibited. Reduced the phosphorylation of mTOR, S6K1 and S6. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Primary rat hepatocytes Concentration: 1, 3, 10, 30, 100 and 300 μM Incubation Time: 5.5 h or 12 h Result: Showed no toxicity at 1-30 μM, decreased cell viability after 12 h incubation at 100 μM. |
| In Vivo | Coronarin A (30 or 100 mg/kg; i.p. or p.o.; once daily for 22 days) ameliorates hyperglycemia in mice[1]. Coronarin A (100 mg/kg; p.o.; once daily for 22 days) inhibits the mTOR/S6K1 pathway to activate PI3K/Akt and ERK/β-catenin signaling in livers of ob/ob mice[1]. Pharmacokinetic properties of Coronarin A after single administrationa in ob/ob mice[1]. Coronarin A t1/2 (h) tmax (h) Cmax (ng/mL) AUC0-t (ng⋅h/mL) AUC0-∞ (ng⋅h/mL) MRT (h) i.p. 14.8 1.0 1073 4571 11045 21.7 p.o. 3.01 1.0 388 1694 1856 4.88 Data are presented as the mean of three mice. aCoronarin A was intraperitoneally or orally administered at 30 mg/kg to ob/ob mice. Animal Model: Male ob/ob mice[1] Dosage: 30 mg/kg (IP) or 100 mg/kg (PO) Administration: Oral or intraperitoneal administration, once daily for 22 days Result: Significantly decreased the non-fasting and fasting blood glucose. Significantly reduced the serum insulin concentration at 15 min after glucose loading, reduced the average daily food intake while the body weight was unaffected. Increased hepatic glycogen content and the expression levels of gluconeogenic gene Pck1 and G6pc were significantly decreased. Animal Model: Female ob/ob mice[1] Dosage: 30 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal or oral administration (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Result: Intraperitoneal injection exhibited higher plasma exposure than oral gavage at the same dose of 30 mg/kg, with Cmax value of 1073 and 388 ng/mL, respectively. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 401.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 300.435 |
| Flash Point | 196.4±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.208923 |
| PSA | 33.37000 |
| LogP | 5.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|