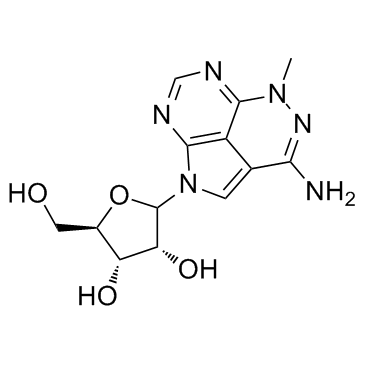
35943-35-2
| Name | triciribine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
triciribine
1,4,5,6,8-Pentaazaacenaphthylen-3-amine, 1,5-dihydro-5-methyl-1-β-D-ribofuranosyl- UNII-2421HMY9N6 5-Methyl-1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,5-dihydro-1,4,5,6,8-pentaazaacenaphthylen-3-amine 1,5-Dihydro-5-methyl-1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,4,5,6,8-pentaazaacenaphthylen-3-amine 1,5-Dihydro-5-methyl-1-b-D-ribofuranosyl-1,4,5,6,8-pentaazaacennaphthylen-3-amine 5-Methyl-1-b-D-ribofuranosyl-1,5-dihydro-1,4,5,6,8-pentaazaacenaphthylen-3-amine API-2 Akt/PKB Signaling Inhibitor-2 Inhibitor V |
| Description | Triciribine is a DNA synthesis inhibitor, also inhibits Akt and HIV-1/2 with IC50 of 130 nM, and 0.02-0.46 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
DNA synthesis Akt:130 nM (IC50, Cell Assay) HIV-1:0.02-0.46 μM (IC50) HIV-2:0.02-0.46 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | The nucleoside analog Triciribine (TCN) is a purine analog which is initially shown to inhibit DNA synthesis. Triciribine selectively inhibits the phosphorylation and activation of all three Akt isoforms. At a concentration of 10 μM Triciribine Akt phosphorylation is inhibited at both Thr308 and Ser473. Triciribine effectively inhibits the phosphorylation and consequently the catalytic activity of Akt in PC-3 cells[1]. The Akt inhibitor Triciribine (TCN) does not effectively inhibit the human cell line U87MG but inhibits other astrocytoma cell lines in a grade-dependent manner. The WHO II K1861-10 line is incompletely inhibited (69% maximum inhibition) with a GI50 value of 1.7 µM for Triciribine. Triciribine exhibits maximum growth inhibition around 1-10 µM and inhibits phosphorylation of Akt, as well as downstream p70S6K, to basal levels at 100 µM (IC50=130 nM) in KR158 cells[2]. Triciribine (TCN) is a novel tricyclic compound with known antitumor activity. Using a syncytial plaque assay, Triciribine is active against HIV-1 at 0.01-0.02 μM. Using a microtiter XTT assay, Triciribine is active against a panel of HIV-1 and HIV-2 strains at IC50 values ranging from 0.02 to 0.46 μM[3]. |
| In Vivo | Triciribine (TCBN) treatment, administered for 7 days after 14 days of hypoxia until 21 days of hypoxia is reached, reversed the vascular thickening as shown by immunohistochemistry and Western analyses. On the other hand, Rapamycin treatment did not prevent hypoxia-induced pulmonary alveolar haemorrhage and congestion. Triciribine partially inhibited progressive pruning of the vasculature, which supports our previous finding that Triciribine alleviates vessel occlusion in microcapillaries. In contrast, Rapamycin treatment did not significantly reverse the reduced vascular density due to chronic hypoxia and had no significant effect on pruning of small vessels[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The human SF295 and U87MG GBM lines and the mouse K1861-10, KR158, and KR130G astrocytoma lines are plated at a density of 2500 cells/100 µL complete media in 96-well plates. Mouse primary astrocytes are plated at 5000 cells/100 µL. Cells are treated in triplicate with serial dilutions of inhibitors (The inhibitors tested are PI-103, Triciribine and Rapamycin) ranging from µM to pM. Cell proliferation is measured after 3 days using the Alamar Blue assay on a Novostar plate reader. Values for 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) and 50% growth inhibitory concentration (GI50) are calculated using standard procedures in GraphPad Prism v4 and Microsoft Excel[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Akt1+/+ and Akt1−/− mice are subjected to normoxia or hypoxia (10% O2) for 7 and 14 days (n=2-6 mice per group). Noteworthy, high mortality is observed in Akt1−/− mice exposed to hypoxia longer than 14-16 days. For pharmacological inhibition studies, Akt1+/+ mice, subjected to normoxia or chronic hypoxia for 14 days, received daily i.p. injection of saline, Triciribine (0.5 mg/kg per day) or Rapamycin (1.5 mg/kg per day) for 7 days, and the total continuous exposure to hypoxia or normoxia is 21 days (n=6-8 mice per group). Pharmacological inhibitors are administered daily while the mice are maintained in the hypoxia chamber to minimize exposure to air and spontaneous reversal of pulmonary remodelling. |
| References |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 718.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H16N6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 320.304 |
| Flash Point | 388.3±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 320.123291 |
| PSA | 144.47000 |
| LogP | -2.70 |
| Appearance | tan |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.928 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >10mg/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| RTECS | RY8455000 |
|---|
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
![4-(1-methylhydrazino)-5-cyano-7-[(2,3,5-tri-O-benzoyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyl]-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/499/699011-59-1.png)
![6-bromo-4-chloro-5-cyano-7-[2,3,5-tri-O-benzoyl-β-D-ribofuranosyl]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/default.png)
![6-bromo-5-cyano-4-(1-methylhydrazino)-7-[2,3,5-tri-O-benzoyl-β-D-ribofuranosyl]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/037/699011-58-0.png)
![6-bromo-4-chloro-5-cyanopyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/324/24391-39-7.png)
![6-Bromo-4-oxo-4,7-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/459/24391-40-0.png)
![4-amino-6-bromo-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/090/19393-83-0.png)
![4-(N-methyl-hydrazino)-7-β-D-ribofuranosyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/080/35943-36-3.png)