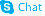207671-50-9
| Name | 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-( 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside trihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Rutin hydrate
MFCD00149490 EINECS 205-814-1 |
| Description | Rutin hydrate is a flavonol glycoside, able to cross the blood-brain barrier, and acts by inhibiting JNK and ERK1/2 activation and activating mTOR signalling. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
JNK ERK1 ERK2 mTOR |
| In Vivo | Rutin hydrate (100 mg/kg) significantly lowers MDA levels and concomitantly increases glutathione (GSH), GSH/oxidized glutathione (GSSG) ratio, total glutathione levels and activities of GPx in the brain of rats. Rutin hydrate alone or in combination with a-tocopherol to CdCl2 intoxicated rats inhibits the declines in the levels of Ach and ChAT activity and significantly inhibited the activities of AChE. Rutin hydrate also inhibits neural apoptosis by inhibiting JNK activation in the brain of control and CdCl2 intoxicated rats and of ERK1/2 activation in the brain of CdCl2 intoxicated rats. In addition, Rutin hydrate activates mTOR/Akt in the brain of control and CdCl2 intoxicated rats[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] (1) A control group receives of 0.01 g/mL carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) dissolved in distilled water; (2) α-tocopherol acetate treated group: control rats receive α-tocopherol (120 IU/rat) diluted in 0.1 mL of coconut oil; (3) Rutin hydrate treated control group (control + Rutin hydrate): control rats receive Rutin hydrate (100 mg/kg); (4) CdCl2 intoxicated group receives CdCl2 at a final dose of 5 mg/kg to induce neurotoxicity; (5) CdCl2 + Rutin hydrate treated group (CdCl2 + Rutin hydrate) receives CdCl2 (5 mg/kg) and receives a coincided dose of Rutin hydrate (100 mg/kg body weight); (6) CdCl2 + Rutin hydrate + α-tocopherol acetate-treated group receives CdCl2 (5 mg/kg) and receives concomitant dose of Rutin hydrate (100 mg/kg) in conjugation with α-tocopherol acetate (120 IU/rat) that is diluted in 0.1 mL of coconut oil. All treatments are given by orogastric gavage with a polyethylene catheter PE 190 daily for 30 days[1]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 195°C dec. (Lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H3O16.xH2O |
| Molecular Weight | 664.56300 |
| Exact Mass | 664.18500 |
| PSA | 297.12000 |