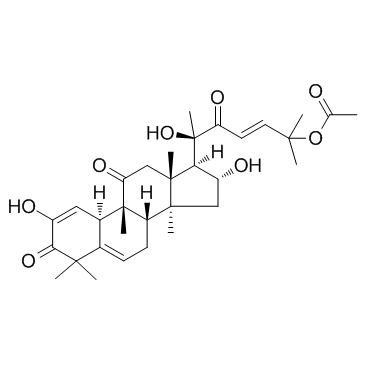
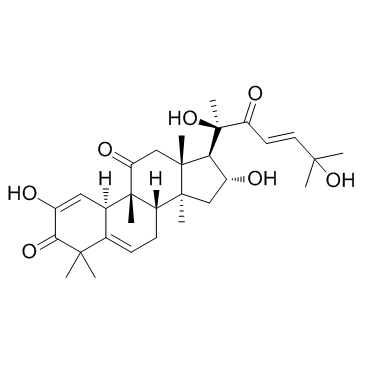
18444-66-1
| Name | Cucurbitacin E |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(9b,10a,16a,23E)-25-(Acetyloxy)-2,16,20-trihydroxy-9-methyl-19-norlanosta-1,5,23-triene-3,11,22-trione
(3E,6R)-6-[(8S,9R,10R,13R,14S,16R,17R)-2,16-Dihydroxy-4,4,9,13,14-pentamethyl-3,11-dioxo-4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-6-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-oxo-3-hepten-2-ylacetat 19-Norlanosta-1,5,23-triene-3,11,22-trione, 25-(acetyloxy)-2,16,20-trihydroxy-9-methyl-, (9β,10α,16α,23E)- Acétate de (4R,9β,16α,23E)-2,16,20-trihydroxy-9,10,14-triméthyl-1,11,22-trioxo-4,9-cyclo-9,10-secocholesta-2,5,23-trién-25-yle α-Elaterin 25-(Acetyloxy)-2b,16a,20-trihydroxy-9b-methyl-19-nor-10a-lanosta-1,5,23E-triene-3,11,22-trione (3E,6R)-6-[(8S,9R,10R,13R,14S,16R,17R)-2,16-Dihydroxy-4,4,9,13,14-pentamethyl-3,11-dioxo-4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-6-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-oxo-3-hepten-2-yl acetate Cucurbitacin E A-Elaterin CUCURBITACIN E(SH) Acétate de (3E,6R)-6-[(8S,9R,10R,13R,14S,16R,17R)-2,16-dihydroxy-4,4,9,13,14-pentaméthyl-3,11-dioxo-4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodécahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phénanthrén-17-yl]-6-hydroxy-2-méthyl-5-oxo-3-heptèn-2-yle α-Elaterine 19-Nor-9β,10α-lanosta-1,5,23-triene-3,11,22-trione, 2,16α,20,25-tetrahydroxy-9-methyl-, 25-acetate (8CI) (4R,9β,16α,23E)-2,16,20-Trihydroxy-9,10,14-trimethyl-1,11,22-trioxo-4,9-cyclo-9,10-secocholesta-2,5,23-trien-25-yl acetate (4R,9β,16α,23E)-2,16,20-Trihydroxy-9,10,14-trimethyl-1,11,22-trioxo-4,9-cyclo-9,10-secocholesta-2,5,23-trien-25-ylacetat Estra-1,5-diene-3,11-dione, 17-[(1R,3E)-5-(acetyloxy)-1-hydroxy-1,5-dimethyl-2-oxo-3-hexen-1-yl]-2,16-dihydroxy-4,4,9,14-tetramethyl-, (9β,10α,16α,17β)- 25-acetate cucurbitacine-e |
| Description | Cucurbitacin E is a natural compound which from the climbing stem of Cucumic melo L. Cucurbitacin E significantly suppresses the activity of the cyclin B1/CDC2 complex. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
cyclin B1/CDC2 Autophagy |
| In Vitro | To explore the antitumor activity of Cucurbitacin E (CuE) against colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, an in vitro study is initiated in which each of the CRC cell lines is exposed to increasing doses of Cucurbitacin E (0, 2.5, 5, and 7.5 μM) over a period of 24 h. The proliferation of the Cucurbitacin E-treated cancer cells is then measured using the MTT method. Cucurbitacin E is shown to induce morphological changes in the primary colon cancer cells. Microscopic observation showed that following exposure to Cucurbitacin E (5 μM) between 6 and 24 h, the primary colon cancer cells underwent a remarkable change in morphology. Cucurbitacin E inhibits tumor growth by arresting the cell cycle in the G2/M phase via GADD45γ gene expression and the blockage of cyclin B1/CDC2 complex in primary CRC cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | A high fat diet mice model of metabolic syndrome (HFD-MetS) is developed to assess the role of Cucurbitacin E (CuE) on body weight and fat tissue biology. Significant decrease in body weights of HFD-MetS mice treated with Cucurbitacin E (0.5mg/kg) are found as compared to HFD-MetS mice treated with vehicle alone. Cucurbitacin E treatment reduces all fat pads weights in HFD-MetS mice. 55% reduction is observed in total fat in mice, after treatment with Cucurbitacin E in comparison to HFD-MetS mice. Abdominal obesity is strongly associated with metabolic syndrome. Central obesity is reduced to 50% after Cucurbitacin E treatment as compared to HFD MetS mice, elucidating the effectiveness of Cucurbitacin E in targeting MetS[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The colorectal cancer (CRC) cells are seeded into 96-well culture plates at 5000 cells/well. The cells are treated with 0, 2.5, 5, and 7.5 μM Cucurbitacin E for 1-3 days. MTT dye (1 mg/mL) is added to each well for at least 4 h of treatment. The reaction is stopped by the addition of DMSO, and optical density is measured at 540 nm on a multi-well plate reader. Background absorbance of the medium in the absence of cells is subtracted. All samples are assayed in triplicate, and the mean for each experiment is calculated. Results are expressed as a percentage of control, which is considered as 100%. Each assay is carried out in triplicate, and the results are expressed as the mean[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] C57BL/6 male mice are used. The mice are designated as metabolic syndrome mice (HFD-MetS-mice). Briefly, the mice are randomly assigned into two groups according to their diet for 8 weeks (n = 10-12): high fat diet group (HFD) (60% fat, 20% carbohydrate, 20% protein) or the matched low fat, standard diet group (SD) (10% fat, 70% carbohydrate, 20% protein). After eight weeks on high fat diet, the mice with significant obese phenotype and fasting blood glucose levels ≥126 mg/dL are considered MetS mice. The MetS mice are continued on the HFD throughout the study. The MetS mice are then randomly divided into three additional groups, according to the treatment administered by oral gavage for 10 weeks (n=10-12): a low dose 0.25 mg/kg/day of Cucurbitacin E designated as HFD+Cucurbitacin E (L) or high dose 0.5 mg/kg/day of Cucurbitacin E, designated as HFD+Cucurbitacin E (H) or 50 mg/kg/day Orlistat (HFD+Orlistat). Animals on SD are administered 0.5% CMC by oral gavage[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 712.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 228-234ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C32H44O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 556.687 |
| Flash Point | 224.4±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 556.303589 |
| PSA | 138.20000 |
| LogP | 3.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 25 |
| Safety Phrases | 1-22-45-24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 3172 |
| RTECS | RC6305500 |
| HS Code | 29153900 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |