83-86-3
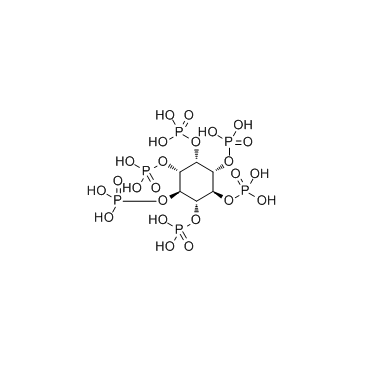
| Name | myo-inositol hexakisphosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakis-dihydrogenphosphate
Phytine Phyticacid Fytic acid inositol hexakisphosphate Alkalovert myo-Inositol hexaphosphate (2,3,4,5,6-pentaphosphonooxycyclohexyl) dihydrogen phosphate Inositol hexaphosphate Phytate myo-inositol 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate Alkovert 1,2,3,4,5,6-Cyclohexanehexol, hexakis(dihydrogen phosphate), sodium salt (1:12) Acidum fyticum MFCD00082309 Dodecasodium 1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexayl hexakis(phosphate) EINECS 201-506-6 |
| Description | Phytic acid is a major phosphorus storage compound of most seeds and cereal grains. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Phytic acid, a major phosphorus storage compound of most seeds and cereal grains, contributes about 1 to 7% of their dry weight. It may account for more than 70% of the total kernel phosphorus. Phytic acid has the strong ability to chelate multivalent metal ions, especially zinc, calcium, and iron. The binding can result in very insoluble salts that are poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, which results in poor bioavailability of minerals. Phytic acid is also considered to be a natural antioxidant and is suggested to have potential functions of reducing lipid peroxidation and as a preservative in foods[1]. Phytic acid inhibits the formation of uric acid from xanthine with an IC50 of about 30 mM. The generation of the superoxide is greatly affected by phytic acid; the IC50 is about 6 mM, indicating that the superoxide generating domain of XO is more sensitive to phytic acid[2]. There has been observed an inhibition of tumor growth and induction of cell differentiation in the presence of phytic acid in a few cancer cell lines including colon, nipple, breast, prostate, cervix, liver, pancreas, melanoma and glioblastoma[3]. |
| In Vivo | Phytic acid has a neuroprotective effect in MPTP-induced PD model and the neuroprotection is correlated with its anti-inflammatory effect which may be associated with suppression of pathways that involved in NF-κB and p-ERK. Phytic acid significantly inhibits MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell loss in the substantia nigra (SN). Moreover, using immunohistochemistry method and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), microglial activation and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) are found to be markedly repressed by phytic acid[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: MPTP (20 mg/kg/day, i.p.) is administrated for 5 days and animals are killed at 7 days later. Phytic acid (30 mg/kg/day, i.p.) or normalsaline is injected 4 days before MPTP administration and con-tinued until mice are killed, reaching a total treatment period of16 days[4]. |
| References |
[1]. Zhou JR, et al. Phytic acid in health and disease. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1995 Nov;35(6):495-508. |
| Density | 2.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1190.7±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H18O24P6 |
| Molecular Weight | 660.04 |
| Flash Point | 673.9±37.1 °C |
| PSA | 459.42000 |
| LogP | -8.47 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.629 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H290-H314-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P280-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | 1760 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | NM7525000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 2919900090 |
|
~% 
83-86-3 |
| Literature: Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'Academie des Sciences, , vol. 169, p. 138 Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 4, p. 158 |
|
~% 
83-86-3 |
| Literature: Helvetica Chimica Acta, , vol. 4, p. 164 |
| HS Code | 2919900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2919900090 other phosphoric esters and their salts, including lactophosphates; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives。supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |