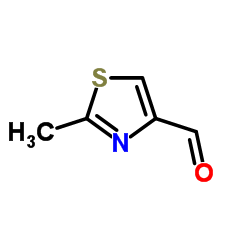
152044-54-7
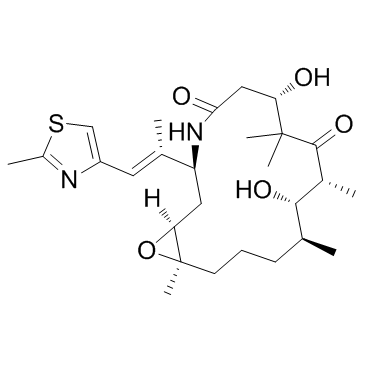
| Name | epothilone B |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Epothilone B
(-)-Epothilone B (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-Dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(1E)-1-methyl-2-(2-methyl-4-thiazolyl)ethenyl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione 4,17-Dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione, 7,11-dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(E)-1-methyl-2-(2-methyl-4-thiazolyl)ethenyl]-, (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)- Epothilon B EPO906,EpoB,Patupilone EPO906 [1R*,3R*(E),7R*,10S*,11R*,12R*,16S*]-7,11-dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[1-methyl-2-(2-methyl-4-thiazolyl)ethenyl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(E)-1-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione GNF-PF-193 UNII-UEC0H0URSE Epothilone B (EPO906,Patupilone) Patupilone (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-Dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(1E)-1-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1-propen-2-yl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione (1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7,11-Dihydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-[(1E)-1-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione EpoB |
| Description | Epothilone B is a microtubule stabilizer with a Ki of 0.71μM. It acts by binding to the αβ-tubulin heterodimer subunit which causes decreasing of αβ-tubulin dissociation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC0.01: 1.8 μM (Microtubule/Tubulin)[1] |
| In Vitro | Epothilone B inhibits HCT116 cells with IC50 of 0.8 nM in HCT-116 cell line cytotoxicity assay[1]. Epothilone B (Patupilone) is a microtubule (MT) targeting agent. As shown by MTT cell proliferation assay, after 72 h of treatment Epothilone B efficiently inhibits cell growth with an IC50 of 6 nM, while concentrations ≤1 nM are not cytotoxic. Epothilone B significantly inhibits transwell cell migration at the non-cytotoxic concentration of 1 nM, and the effect is more evident at 10 nM[2]. Epothilone B (Patupilone) is a novel, non-taxane-related and nonneurotoxic microtubule-stabilizing agent in human medulloblastoma cell lines. Epothilone B reduces the proliferative activity in the D341 cell line, with an IC50 of 0.53 nM; in the D425Med cell line, with an IC50 of 0.37 nM; and in the DAOY cell line, with an IC50 of 0.19 nM. In the D341Med cell line, the effect of Epothilone B on clonogenic survival is at dose range of Epothilone B similar to the level of proliferative activity and viability (IC50, 0.50-0.75 nM). However, the clonogenicity of D425Med and DAOY cells is already strongly reduced at a 10-fold lower concentration of Epothilone B (IC50, 30 pM). These results overall demonstrate that Epothilone B is highly potent against different medulloblastoma cell lines[3]. |
| In Vivo | Treatment with Epothilone B (Patupilone) or ionizing radiation alone results in a partial tumor growth suppression over 10 days, whereas combined treatment exerts a strong supra-additive tumor growth control, with complete tumor regression in the follow-up period (P<0.005, for ionizing radiation or Epothilone B alone vs combined treatment)[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Asp-Glu-Val-Asp (DEVD)ase activity is determined in cytosolic cell extracts. Cells are treated with increasing concentrations of Epothilone B (Patupilone) for 6, 12, 24, and 48 h. Cells are harvested thereafter by trypsin/EDTA, centrifuged, and washed with precooled PBS. The cell pellet is suspended in 5 volumes of precooled buffer A (20 mM HEPES-KOH [pH 7.5], 10 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM sodium EDTA, 1 mM sodium EGTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol [DDT], 250 mM sucrose, and 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride [PMSF] supplemented with protease inhibitors [5 mg/mL pepstatin A, 10 mg/mL leupeptin, 2 mg/mL aprotinin, 2 mg/mL DTT, and 1 mM of PMSF]). After incubation on ice for 15 min, the cells are disrupted by freezing and thawing. Cell lysates are centrifuged at 1000g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatant is further centrifuged at 100 000g for 30 min. The resulting supernatant (S-100 fraction) is stored at −80°C. To determine caspase 3-like activity, 75 μg of protein from the S-100 fraction is incubated at 37°C with the colorimetric caspase 3 substrate N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp p-nitroanilide (100 mM; Ac-DEVD-pNA) and 1 mM dATP in a final volume of 120 μL. Cleavage of the caspase substrate is monitored at 405 nm using a GenTec spectrophotometer[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Human glioblastoma cells (U87MG, ATCC) are routinely maintained at 37°C and 5% CO2 in EMEM medium, with NEAA, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM of glutamine, 1% penicillin and streptomycin. U87MG cells are used for no more than 15 passages. Cells are seeded in 96-well plates (5000 cells/well). After 24 h cells are treated with Epothilone B. Growth inhibition of U87MG cells is measured after 72 h of drug treatment by using the MTT cell proliferation assay[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] D425Med cells (6×106) are injected subcutaneously on the backs of 4-6-week-old athymic nude mice. Tumor volumes are determined from caliper measurements of tumor length (L) and width (l) according to the formula (L×l2)/2. Tumors are allowed to expand to a volume of 200 mm3 (±10%) before treatment start. With the use of a customized shielding device, mice are given strictly loco regional radiotherapy of 3×3 Gy on 3 consecutive days using a Gulmay 200 kV X-ray unit at 100 cGy/min at room temperature. Epothilone B (2 mg/kg; dissolved in 30% PEG-300/70% saline) is applied intravenously 24 h before the first treatment with ionizing radiation (at day 0 of the treatment; n=5 per group). Tumor growth is monitored daily. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 680.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-97ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H41NO6S |
| Molecular Weight | 507.682 |
| Flash Point | 365.2±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 507.265472 |
| PSA | 137.49000 |
| LogP | 2.29 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.532 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 29419090 |
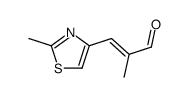
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |



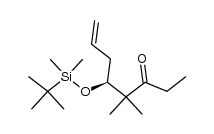
![(-)-(2Z,5S,6E)-5-{[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy}-2,6-dimethyl-7-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)hepta-2,6-dien-1-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/378/218614-16-5.png)

![(1S,3S,7S,10R,11S,12S,16R)-7-((tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)-11-hydroxy-8,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-((E)-1-(2-methylthiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl)-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadecane-5,9-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/400/355387-09-6.png)