D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-13 17:34:45
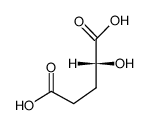
D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid structure
|
Common Name | D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13095-47-1 | Molecular Weight | 148.11400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acidD-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid ((R)-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid) is the principal metabolite accumulating in neurometabolic disease D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid is a weak competitive antagonist of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and inhibits multiple α-KG-dependent dioxygenases with a Ki of 10.87 mM. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid binds and inhibits ATP synthase and inhibits mTOR signaling[1][2][3][4][5]. |
| Name | (2R)-hydroxyglutaric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid ((R)-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid) is the principal metabolite accumulating in neurometabolic disease D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid is a weak competitive antagonist of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and inhibits multiple α-KG-dependent dioxygenases with a Ki of 10.87 mM. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid binds and inhibits ATP synthase and inhibits mTOR signaling[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 10.87 mM (α-KG-dependent dioxygenases)[1] ATP synthase[2] mTOR[2] Reactive oxygen species (ROS) [5] |
| In Vitro | D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid ((R)-2-hydroxyglutarate) accumulates in human cancers carrying neomorphic mutations in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 and 2 genes[1][2]. A partial inhibition of KDM7A toward both H3K9me2 and H3K27me2 peptides is observed in the presence of 50 mM D-2-HG and 100 μM α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). Addition of 300 μM α-KG is capable of reversing the inhibition of Caenorhabditis elegans KDM7A (CeKDM7A) by 50 mM D-2-HG, indicating that D-2-HG is a weak competitive inhibitor against α-KG toward the CeKDM7A demethylase[1]. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid is a weak inhibitor of TET hydroxylases. In the presence of 0.1 mM of α-KG, addition of 10 mM D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid results in a partial (33%) inhibition of TET2 and addition of 50 mM D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid results in more inhibition (83%) of TET2. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid exhibits a less pronounced inhibitory effect toward TET1[1]. |
| In Vivo | D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid strongly inhibits glucose utilization, CO2 production and the respiratory chain in rat cerebral cortex and human skeletal muscle, as well as in submitochondrial particles from bovine heart, suggesting an impairment of the aerobic metabolism[5]. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid has also been proposed as an endogenous excitotoxic organic acid because it significantly decreased cell viability in neuronal cultures from chick embryo telencephalons and from neonatal rat hippocampus through stimulation of specific NMDA glutamate receptors[5]. D-α-Hydroxyglutaric acid (0.01-1 mM) significantly increases chemiluminescence and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBA-RS) and decreased total antioxidant reactivity (TAR) values in the cortical supernatants in 30-day-old-rats[5]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 148.11400 |
| Exact Mass | 148.03700 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| D-2-Hydroxyglutarate |
| D-2-hydroxyglutarate |
| D-2HG |
| D-(+)-2-hydroxyglutaric acid |
| D-2-hydroxyglutaric acid |
| R-(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate |
| 2-hydroxypentanedioic acid |