Telmisartan
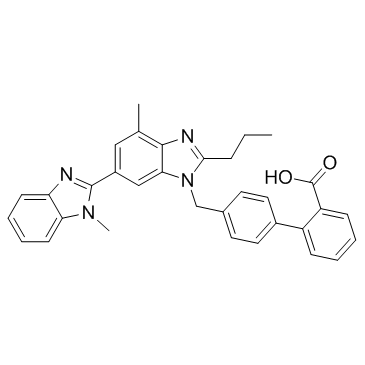
Telmisartan structure
|
Common Name | Telmisartan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 144701-48-4 | Molecular Weight | 514.617 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 771.9±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C33H30N4O2 | Melting Point | 261-263°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 420.6±35.7 °C | |
Use of TelmisartanTelmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM. |
| Name | telmisartan |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 9.2 nM (angiotensin II type 1 receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | In intact RVSMC cells and in membrane preparations, telmisartan inhibits the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 9.2 ± 0.8 nM. In the same experimental conditions, angiotensin II displaces 125I-AngII with an IC50 value of 2.9 ± 0.5 nM. The specific binding of [3H]telmisartan to SMC membranes is displaced by unlabeled telmisartan with an IC50 of 7.7 ± 1.8 nM and by cold AngII with an IC50 of 32.7 ± 5.7 nM [1]. Telmisartan treatment (100 μM) reduces the proliferation of three EAC cell lines (OE19, OE33, and SKGT-4), induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase and regulates cell cycle-related proteins in EAC cells, and induces the phosphorylation of AMPK and regulates cell cycle-related proteins via the AMPK/mTOR pathway in EAC cells. Telmisartan inhibits the activation of RTKs, downstream effectors and cell cycle-related proteins[5]. |
| In Vivo | In the telmisartan (0.1, 0.3, and 1 mg/kg)-treated rats, the specific binding of [3H]telmisartan to the surface of living RVSMC is saturable and increases quickly to reach equilibrium within 1 h. Telmisartan dissociates very slowly from the receptor with a dissociation half-life (t1/2) of 75 min, which is comparable with candesartan and almost 5 times slower than angiotensin II (AngII). In vivo, telmisartan blunts the blood pressure response to exogenous AngII dose dependently[1]. Telmisartan (10 mg/kg/d) administration effectively suppresses aneurysm pathogenesis after PPE infusion as well, regardless of whether treatment is initiated before or after aneurysm creation or continues for a limited or extended time. Telmisartan treatment is associated with reduced messenger RNA levels for CCL5 and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in aneurysmal aortae, with no apparent effect on PPARγ-regulated gene expression[2]. Telmisartan (1 mg/kg/day) significantly ameliorates neuronal loss and the spatial acquisition impairment in 5XFAD mice, but without any changes of NeuN expression in the hippocampus layer. Telmisartan (1 mg/kg/day) treatment reduces amyloid burden and microglial accumulation in 5XFAD mice brain, induces microglial polarization towards neuroprotective phenotype, but does not alter the expression levels of NEP and IDE in 5XFAD mice specific brain areas[3]. Telmisartan (0.05, 0.1, 1 mg/kg, p.o.) shows significant reduction in immobility time, antagonizes depression and anxiety, and also significantly attenuates serum cortisol, NO, IL-6 and IL-1β in rats[4]. Telmisartan (50 μg, i.p.) leads to a 73.2% reduction in tumor growth in mice bearing xenografts derived from OE19 cells. Furthermore, miRNA expression is significantly altered by telmisartan in vivo[5]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell proliferation is assayed using the CCK-8 cell counting kit. Briefly, 5×103 cells are seeded into each well of a 96-well plate and cultured in 100 μL of RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS. After 24 h, ARBs (telmisartan, irbesartan, losartan, and valsartan at 0, 1, 10, or 100 μM) or vehicle is added to each well, and cells are cultured for an additional 48 h. CCK-8 reagent (10 μL) is added to each well, and the plates are incubated at 37°C for 3 h. The absorbance is measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. |
| Animal Admin | Male athymic mice (BALB/c-nu/nu; 6 weeks old; 20-25 g) are maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions using a laminar airflow rack. The mice have continuous free access to sterilized (γ-irradiated) food and autoclaved water. Each mouse is subcutaneously inoculated with OE19 cells (5×106 cells per animal) in the flank. One week later, the xenografts are identifiable as masses with a maximal diameter > 4 mm. The animals are randomly assigned to treatment with telmisartan (50 μg per day) or diluent only (control). The telmisartan group is intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected five times per week with 2 mg/kg telmisartan for four weeks; the control group is administered 5% DMSO alone for four weeks. Tumor growth is monitored daily by the same investigators, and tumor size is measured weekly. The tumor volume (mm3) is calculated as the tumor length (mm) × tumor width (mm)2/2. All animals are sacrificed on day 22 after treatment, and all animals survive during this period. Between-group differences in tumor growth are analyzed by two-way ANOVA. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 771.9±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 261-263°C |
| Molecular Formula | C33H30N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 514.617 |
| Flash Point | 420.6±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 514.236877 |
| PSA | 72.94000 |
| LogP | 7.73 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.667 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
|
Preventing leptin resistance by blocking angiotensin II AT1 receptors in diet-induced obese rats.
Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(3) , 857-68, (2015) AT1 receptor blockers (ARBs) represent an approach for treating metabolic syndrome due to their potency in reducing hypertension, body weight and onset of type 2 diabetes. The mechanism underlying ARB... |
|
|
Behavior of sartans (antihypertensive drugs) in wastewater treatment plants, their occurrence and risk for the aquatic environment.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21(18) , 10830-9, (2014) Pharmaceuticals and other anthropogenic trace contaminants reach wastewaters and are often not satisfactorily eliminated in sewage treatment plants. These contaminants and/or their degradation product... |
|
|
Preconcentration of indapamide from human urine using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction.
J. Sep. Sci. 38 , 3090-5, (2015) A simple, sensitive, and selective molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and spectrophotometric method has been developed for the clean-up and preconcentration of indapamide from human urine. M... |
| Kinzalmono |
| Micardis |
| 4'-[(1,7'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-1H,3'H-2,5'-bibenzimidazol-3'-yl)methyl]biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00929085 |
| 4'-[(1,7'-Dimethyl-2'-propyl-1H,3'H-2,5'-bibenzimidazol-3'-yl)methyl]-2-biphenylcarboxylic acid |
| [1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid, 4'-[(1,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl[2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1'-yl)methyl]- |
| Pritor |
| Telmisartan |
| EINECS 620-494-7 |
![4'-((1,7'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-1H,3'H-[2,5'-bibenzo[d]imidazol]-3'-yl)methyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/303/515815-48-2.png) CAS#:515815-48-2
CAS#:515815-48-2 CAS#:915124-86-6
CAS#:915124-86-6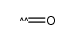 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2![3'-((2'-bromobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-1,7'-dimethyl-2'-propyl-1H,3'H-2,5'-bibenzo[d]imidazole Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/351/1206701-77-0.png) CAS#:1206701-77-0
CAS#:1206701-77-0![4'-[(1,4'-Dimethyl-2'-propyl[2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1'-yl)methyl]-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-carbonitrile Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/083/144702-27-2.png) CAS#:144702-27-2
CAS#:144702-27-2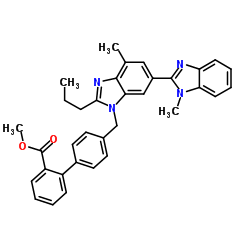 CAS#:528560-93-2
CAS#:528560-93-2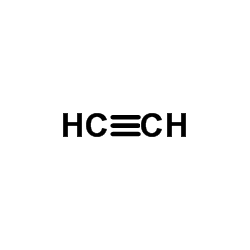 CAS#:74-86-2
CAS#:74-86-2![4'-[[1,4'-Dimethyl-2'-propyl(2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol)-1'-yl]-methyl]-1,1'-biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/121/144702-26-1.png) CAS#:144702-26-1
CAS#:144702-26-1
