Diosmin
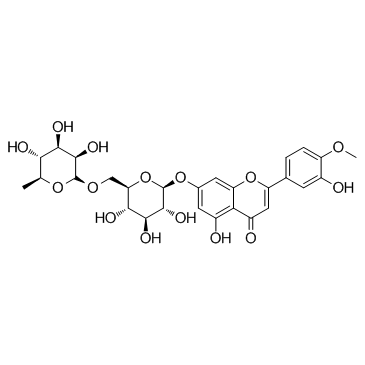
Diosmin structure
|
Common Name | Diosmin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 520-27-4 | Molecular Weight | 608.545 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 926.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32O15 | Melting Point | 277-278°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 305.2±27.8 °C | |
Use of DiosminDiosmin is a flavonoid found in a variety of citrus fruits and also an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). |
| Name | diosmin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Diosmin is a flavonoid found in a variety of citrus fruits and also an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
AhR[1] |
| In Vitro | Treatment with Diosmin causes a dose dependent increase in the amount of adducts formed (up to a 7-fold increase in adducts at 5 μM Diosmin). At 5 μM, Diosmin increases the cytotoxicity of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA), shifting the IC50 of DMBA from an estimated 1.2 μM to 400 nM. Diosmin is not cytotoxic in itself at the concentrations tested. Diosmin causes an increase in CYPIAI activity in MCF-7 cells in a time- and dose-dependent fashion. Diosmin causes a dose-dependent increase in CYPIAI mRNA after 24 h of incubation, causes a long-lasting increase in CYPIAI mRNA accumulation that reaches its peak after 48 h of incubation[1]. |
| In Vivo | Diosmin significantly decreases the malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and increases the activities of total-superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) in the retina of rats compare with the ischemia group (P<0.05), and suppresses the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced reduction in the a- and b-wave amplitudes of the electroretinograms (ERGs) (P<0.05). The thickness of the entire retina, inner nuclear layer, inner plexiform layer, and outer retinal layer and the number of cells in the ganglion cell layer are significantly less after I/R injury (P<0.05), and Diosmin remarkably ameliorates these changes on retinal morphology. Diosmin also attenuates the I/R-induced loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) of the rat retina (P<0.05)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | MCF-7 cells are plated at 25,000 cells/well in 24-well plates. After 24 h, the medium is changed to medium containing 5 μM Diosmin. After an additional 24 h, the medium is again changed with medium containing 5 μM Diosmin. After 3 days, the total cell growth is assessed by sulforhodamine[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Healthy male Wistar rats (n=112) weighing 180 to 200 g each are used in this study. The animals are randomly assigned to the following 4 groups, which include combinations of the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury model or sham injury with the i.g. administration of Diosmin or vehicle solution: sham+vehicle (SV) group, sham+Diosmin (SD) group, model+vehicle (MV) group, and model+Diosmin (MD) group. For intragastric administration, 5 mL of 2% Diosmin per kilogram weight of the rat, or the same volume of vehicle solution, is administered intragastrically 30 min before the onset of ischemia, and then daily after I/R injury until the animals are sacrificed. Using an overdose of anesthesia, 8 rats from each group are sacrificed 24 h after I/R injury, and their eyeballs harvested for determination of the malondialdehyde (MDA) level and the activities of total-superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT). At 7 days post-I/R injury, electroretinograms (ERGs) are recorded in 6 rats per group. Meanwhile, 6 rats in each group are randomly chosen for retrograde labeling of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) , and the remaining 8 rats from each group are histopathologically examined[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 926.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 277-278°C |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 608.545 |
| Flash Point | 305.2±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 608.174133 |
| PSA | 238.20000 |
| LogP | 2.05 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.712 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36-36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Diosmin induces genotoxicity and apoptosis in DU145 prostate cancer cell line.
Toxicol. In Vitro 29(3) , 417-25, (2015) Plant-derived dietary polyphenolic compounds, such as flavonoids, with cancer cell-specific pro-apoptotic activity and chemopreventive potential are thought to be promising anticancer agents. In the p... |
|
|
Amino acid, mineral, and polyphenolic profiles of black vinegar, and its lipid lowering and antioxidant effects in vivo.
Food Chem. 168 , 63-9, (2014) Black vinegar (BV) contains abundant essential and hydrophobic amino acids, and polyphenolic contents, especially catechin and chlorogenic acid via chemical analyses. K and Mg are the major minerals i... |
|
|
Flavonoids are inhibitors of human organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1)-mediated transport.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(9) , 1357-66, (2014) Organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) has been reported to be involved in the nephrotoxicity of many anionic xenobiotics. As current clinically used OAT1 inhibitors are often associated with safety issue... |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-yl-6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| UNII-7QM776WJ5N |
| Venosmine |
| EINECS 208-289-7 |
| 3',5,7-trihydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone 7-rutinoside |
| Diosmin |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 7-((6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)- |
| 7-[[6-O-6-Deoxy-a-L-mannopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-b-rutinosyloxy-4H-chromen-4-one |
| Ven-Detrex |
| 3',5,7-Trihydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone-7-rutinoside |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-({[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4H-chromen-4-on |
| Veno-V |
| MFCD00009772 |
| 5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-(O6-a-L-rhamnopyranosyl-b-D-glucopyranosyloxy)chromen-4-one |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 7-((6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β- D-glucopyranosyl)oxy)-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)- |
| Diosmine |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 7-[[6-O-(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)- |
| Diosmetin 7-b-Rutinoside |
| Diosimin |
| diosmetin-7-rhamnoglucoside |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-({[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4H-chromen-4-one |
| 5-Hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-méthoxyphényl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-({[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-méthyltétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}méthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4H-chromén-4-one |
| Barosmin |
 CAS#:520-26-3
CAS#:520-26-3![(2R,3Ξ)-5-acetoxy-2-(3-acetoxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-3-bromo-7-[O2,O3,O4-triacetyl-O6-(tri-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy]-chroman-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/262/69081-76-1.png) CAS#:69081-76-1
CAS#:69081-76-1 CAS#:480-44-4
CAS#:480-44-4 CAS#:5128-44-9
CAS#:5128-44-9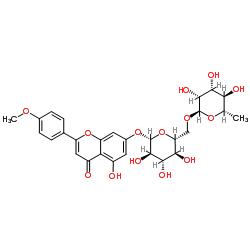 CAS#:480-36-4
CAS#:480-36-4 CAS#:520-34-3
CAS#:520-34-3
