| Description |
Bradykinin is an active peptide that is generated by the kallikrein-kinin system. It is a inflammatory mediator and also recognized as a neuromediator and regulator of several vascular and renal functions.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Bradykinin is a potent vasodilator peptide that exerts its vasodilatory action through stimulation of specific endothelial B2 receptors, thereby causing the release of prostacyclin, NO, and EDHF[1]. Bradykinin has been reported to be involved in the progression of many types of cancer. Bradykinin treatment promotes the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells. Bradykinin treatment stimulates ERK1/2 activation and IL-6 production[2]. Exogenous bradykinin markedly inhibits TF expression in mRNA and protein level induced by LPS in a dose-dependent manner. The NO synthase antagonist L-NAME and PI3K inhibitor LY294002 dramatically abolish the inhibitory effects of bradykinin on tissue factor expression[3].
|
| In Vivo |
Application of 1 μM bradykinin to the ovary produces significant decreases in heart rate and mean arterial pressure. In vagotomized animals, application of 1 μM bradykinin to the ovary produces bradycardia and hypotension similar to the responses evoked when vagal innervation is intact[4]. Vascular bradykinin can improve pancreatic microcirculation and hemorheology in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. The pancreatic microcirculatory blood flow volume and velocity in the vascular bradykinin treatment group increases gradually after 48 h[5]. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation induced by bradykinin administration reduces the activity of GSK-3β and MAPK, and reduces NF-x03BA;B level in the nucleus, thereby inhibiting TF expression. Consistent with this, intraperitoneal injection of C57/BL6 mice with bradykinin also inhibits the thrombus formation induced by ligation of inferior vena cava[3].
|
| Cell Assay |
SW480 cells are pretreated with different concentrations of bradykinin (0, 0.1, 0.5, 1 μM), and then subjected to invasion and migration assays[2].
|
| Animal Admin |
Rats: Bradykinin acetate is applied topically to the surface of the ovary with a thin piece of cotton (7×7 mm square) soaked with the solution. After application for 30 s, the cotton is removed. Each of the stimuli is delivered to the animal after observing stabilization of heart rate and mean arterial pressure[4]. Mouse: Mice are randomly divided into 3 groups: Sham, Model and Bradykinin. Before surgical procedure, the mice of bradykinin group are intraperitoneally injected with bradykinin (10 mg/kg/d) once a day for three days. After ligation, the mice receive bradykinin injection for another two days and analgesic therapy is performed using buprenorphine at 0.1 mg/kg body weight for 3 days. The mice in other groups receive equal saline as control[3].
|
| References |
[1]. Hornig B, et al. Role of bradykinin in mediating vascular effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors inhumans. Circulation. 1997 Mar 4;95(5):1115-8. [2]. Wang G, et al. Bradykinin stimulates IL-6 production and cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2014 Oct;32(4):1709-14. [3]. Dong R, et al. Exogenous Bradykinin Inhibits Tissue Factor Induction and Deep Vein Thrombosis via Activating the eNOS/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(4):1592-606. [4]. Uchida S, et al. Afferent fibers involved in the bradykinin-induced cardiovascular reflexes from the ovary in rats. Auton Neurosci. 2015 Dec;193:57-62. [5]. Liu LT, et al. Effect of vascular bradykinin on pancreatic microcirculation and hemorheology in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(14):2646-50.
|

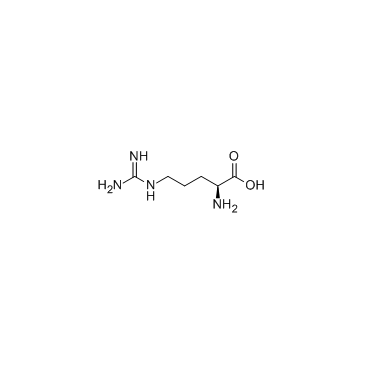 CAS#:74-79-3
CAS#:74-79-3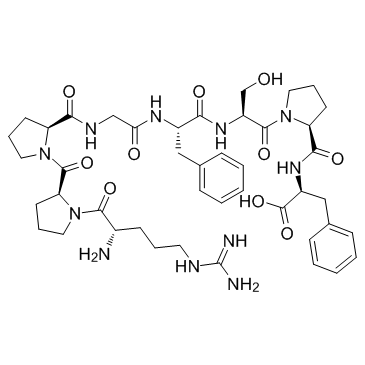 CAS#:15958-92-6
CAS#:15958-92-6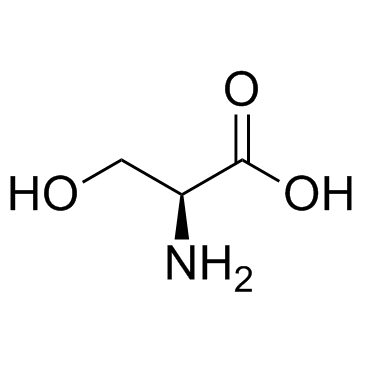 CAS#:56-45-1
CAS#:56-45-1 CAS#:63-91-2
CAS#:63-91-2 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6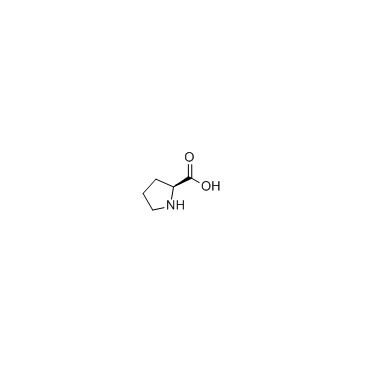 CAS#:147-85-3
CAS#:147-85-3
