H-DL-Pro-OH

H-DL-Pro-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-DL-Pro-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 609-36-9 | Molecular Weight | 115.13 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 252.2±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO2 | Melting Point | 208-210ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 106.3±25.4 °C | |
Use of H-DL-Pro-OHH-DL-Pro-OH is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
| Name | proline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | H-DL-Pro-OH is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 252.2±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 208-210ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 115.13 |
| Flash Point | 106.3±25.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 115.063332 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | -0.57 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.487 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indi... |
|
|
Metabolic network capacity of Escherichia coli for Krebs cycle-dependent proline hydroxylation.
Microb. Cell Fact. 14 , 108, (2015) Understanding the metabolism of the microbial host is essential for the development and optimization of whole-cell based biocatalytic processes, as it dictates production efficiency. This is especiall... |
|
|
Polyhydroxyalkanoates production with Ralstonia eutropha from low quality waste animal fats.
J. Biotechnol. 214 , 119-27, (2015) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are biodegradable and biocompatible polyesters considered as alternatives to petroleum-based plastics. Ralstonia eutropha is a model organism for PHA production. Utilizing... |
| (-)-Proline |
| PROGOITRIN(RG) |
| Proline |
| Proline, L- |
| Proline,DL |
| (-)-(S)-proline |
| (2S)-proline |
| (2S)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid |
| (S)-2-Carboxypyrrolidine |
| (-)-2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid |
| (−)-proline |
| (S)-proline |
| MFCD00005250 |
| EINECS 210-189-3 |
| (2S)-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| DL-Proline 5GR |
| H-DL-PRO-OH |
| (−)-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid |
| (−)-(S)-proline |
| (S)-(-)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| L-a-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic Acid |
| 2-carboxypyrrolidine |
| (S)-(-)-Proline |
| (l)-proline |
| l-Pro |
| H-DL-PYRD(2)-OH |
| pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| (RS)-Proline |
| DL-Prolin |
| L-(-)-proline |
| DL-PROLINE |
| 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid, (S)- |
| (S)-Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
 CAS#:634-97-9
CAS#:634-97-9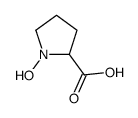 CAS#:36901-87-8
CAS#:36901-87-8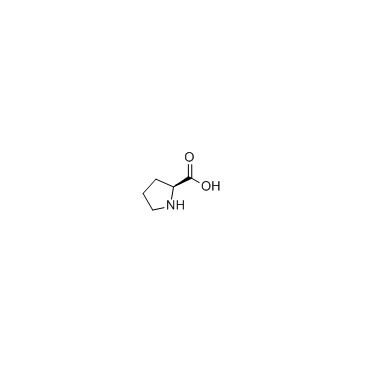 CAS#:147-85-3
CAS#:147-85-3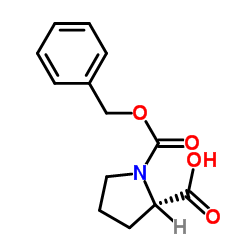 CAS#:1148-11-4
CAS#:1148-11-4 CAS#:138286-85-8
CAS#:138286-85-8 CAS#:75-05-8
CAS#:75-05-8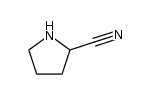 CAS#:57015-08-4
CAS#:57015-08-4 CAS#:344-25-2
CAS#:344-25-2 CAS#:50995-48-7
CAS#:50995-48-7 CAS#:103238-71-7
CAS#:103238-71-7 CAS#:105706-84-1
CAS#:105706-84-1 CAS#:3554-65-2
CAS#:3554-65-2 CAS#:600-18-0
CAS#:600-18-0 CAS#:328-50-7
CAS#:328-50-7 CAS#:51-35-4
CAS#:51-35-4 CAS#:149-87-1
CAS#:149-87-1![Octahydro-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/436/5654-83-1.png) CAS#:5654-83-1
CAS#:5654-83-1![1,3-diazabicyclo[3.3.0]octane-2,4-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/240/5768-79-6.png) CAS#:5768-79-6
CAS#:5768-79-6 CAS#:4333-21-5
CAS#:4333-21-5
