5-Aminosalicylic Acid
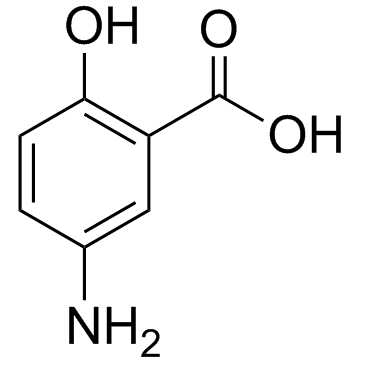
5-Aminosalicylic Acid structure
|
Common Name | 5-Aminosalicylic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 89-57-6 | Molecular Weight | 153.135 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 380.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO3 | Melting Point | 275-280 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 184.1±25.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid5-Aminosalicylic acid acts as a specific PPARγ agonist and also inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and NF-κB. |
| Name | mesalamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5-Aminosalicylic acid acts as a specific PPARγ agonist and also inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and NF-κB. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PPARγ PAK1 p65 |
| In Vitro | 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is a specific agonist for PPARγ, and only PPARγ but not PPARα or PPARδ induces p65 degradation. 5-Aminosalicylic acid induces degradation of p65 protein indicative of PPARγ's E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. 5-Aminosalicylic acid also inhibits PAK1 at the mRNA level which is suggestive of an additional mechanism independent of PPARγ ligand activation. 5-Aminosalicylic acid blocks NF-κB in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) through inhibition of PAK1[1]. Pretreatment with 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) or Nimesulide at different concentration (10-1000 μmol/L) for 12-96 h, inhibits the growth of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells in a dose and time-dependent manner. However, the suppression of 5-Aminosalicylic acid or Nimesulide has no statistical significance. The growth of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells is inhibited dose-dependently when pretreated with different doses of combined 5-Aminosalicylic acid and Nimesulide. Combined 5-Aminosalicylic acid (final concentration 100 μM) and Nimesulide (final concentration 10-1000 μM) inhibits the proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells in a dose-dependent manner, being more potent than corresponding dose of Nimesulide. Similarly, combined Nimesulide (final concentration 100 μM) and 5-Aminosalicylic acid (final concentration 10-1000 μM) also inhibits the proliferation of these cells dose-dependently, being more potent than corresponding dose of 5-Aminosalicylic acid[2]. |
| In Vivo | 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) has an antineoplastic effect in a xenograft tumor model. To evaluate the in vivo antineoplasic effect of 5-Aminosalicylic acid, SCID mice engrafted with HT-29 colon cancer cells are treated daily for 21 consecutive days with 5-Aminosalicylic acid at 50 mM. At the end of the treatment, a reduction of 80-86% of tumor weight and volume is observed in SCID mice receiving 5-Aminosalicylic acid compared with control mice or mice treated with GW9662 alone. The antineoplastic effect of 5-Aminosalicylic acid is already detectable after 10 days of 5-Aminosalicylic acid treatment. Similar results are obtained with mice treated with 5-Aminosalicylic acid at 5 mM. Antitumorigenic effect of 5-Aminosalicylic acid is completely abolished at 21 days by simultaneous intraperitoneal administration of GW9662. Thus, the observed antineoplastic effect of 5-Aminosalicylic acid is at least partially dependent on PPARγ[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Cytostatic effects are measured by MTT assay. HT-29 colon carcinoma cells are detached with a 0.25% trypsin solution for 5 min. Subsequently, the cells are seeded onto 96-well plates (1×106 cells/well), supplemented with 10% FCS and allowed to attach for 24 h before the addition of test compounds (5-Aminosalicylic acid 10, 50, 100, 500, and 1000 μM; Nimesulide; and their combination). Test compounds are diluted in serum-free culture medium. Then the cells are incubated in a medium or at different concentrations of drugs for 48 h, 20 μL of MTT solution (5 g/L) in PBS is added. Four hours later, the medium in each well is removed, and 120 μL of 0.04 mM muriatic isopropanol is added, slightly concussed for 10 min. Dye uptake is measured at 490 nm with an ELISA reader. Five wells are used for each concentration or as a control group. On the other hand, the cells are seeded onto 96-well plates (1×106 cells/well) and allowed to attach for 24 h, then treated with test compounds (5-Aminosalicylic acid, Nimesulide, and their combination). The final concentration is 100 μM. The same medium is added into the control group and dye uptake is then measured. Five wells are used for each test compound or control group[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Six to seven weeks old pathogen-free BALB/c SCID mice are used. Human colon cancer cells (107 HT-29 cells) pretreated or not with GW9662 for 24 h are implanted subcutaneously in the flank of animals. Two days after cell inoculation, mice are treated with 5-Aminosalicylic acid (5 or 50 mM) administered daily by peritumoral injection for 10 or 21 days. The effect of PPARγ during 5-Aminosalicylic acid treatment is evaluated by daily intraperitoneal injection of GW9662 (1 mg/kg/day). The control group receives saline instead of 5-Aminosalicylic acid. Mice are checked three times a week for tumor development. After killing at 10 or 21 days, tumor size and volume are calculated. Tumors are weighted before paraffin embedding for histological examination. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 380.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 275-280 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 153.135 |
| Flash Point | 184.1±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 153.042587 |
| PSA | 83.55000 |
| LogP | 1.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.691 |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | VO1400000 |
| HS Code | 29225000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
|
|
Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the determination of mesalazine in beagle dog plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 29(2) , 261-7, (2015) A simple, specific and sensitive LC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the determination of mesalazine in beagle dog plasma. The plasma samples were prepared by protein precipitation, then t... |
| 5-Aminosalicylic Acid |
| Mesalamine |
| 5-AMINOSALICILIC ACID |
| 5-AMINO SALICYLIC ACID |
| Mesalamine (Lialda) |
| Bactylan |
| Pasalon-rakeet |
| 5-amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Tubersan |
| Salvis |
| Paracipan |
| EINECS 201-919-1 |
| 4-Amino-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
| MFCD00007877 |
| Sanipirol |
| Lepasen |
| PASA |
| 2-Cyanobenzoic acid |
| Pasmicina |
| Benzoic acid, 4-amino-2-hydroxy- |
| Rezipas |
| ZR CQ DVQ |
| Passodico |
| 5-AMINO-2-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID FOR SYNTHESIS |
| 5-Aminosalicylicacid |
| 5-AMINOSALICYLIC ACID (MESALAZINE) |
| 5-Aminosalicglic acid |
| Mesalazine |
| Aminosalicylic Acid |
| 5-AMINOSALICYLIC ACID , CRM STANDARD |
| Aminacyl |
| Paser |
 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9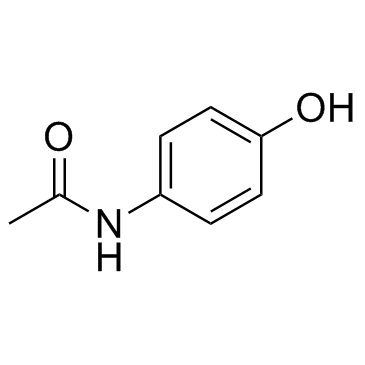 CAS#:103-90-2
CAS#:103-90-2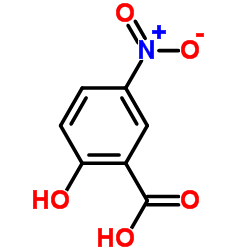 CAS#:96-97-9
CAS#:96-97-9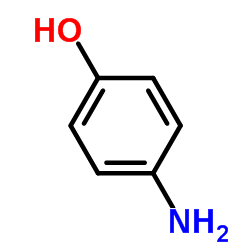 CAS#:123-30-8
CAS#:123-30-8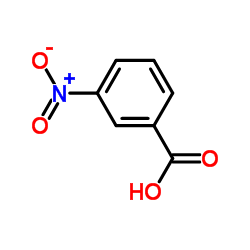 CAS#:121-92-6
CAS#:121-92-6 CAS#:3147-53-3
CAS#:3147-53-3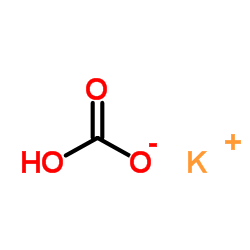 CAS#:298-14-6
CAS#:298-14-6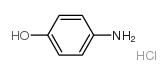 CAS#:51-78-5
CAS#:51-78-5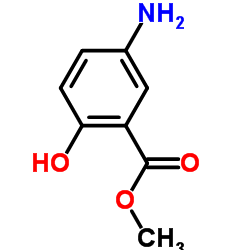 CAS#:42753-75-3
CAS#:42753-75-3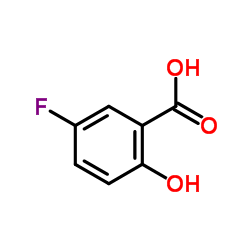 CAS#:345-16-4
CAS#:345-16-4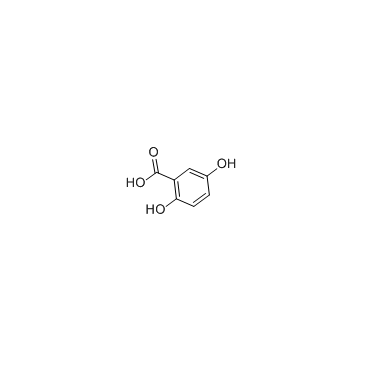 CAS#:490-79-9
CAS#:490-79-9 CAS#:3943-91-7
CAS#:3943-91-7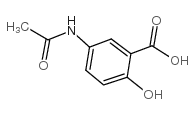 CAS#:51-59-2
CAS#:51-59-2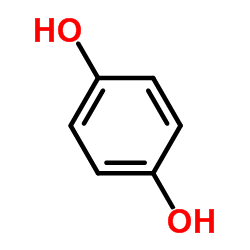 CAS#:123-31-9
CAS#:123-31-9 CAS#:24619-05-4
CAS#:24619-05-4
