88642-46-0
| Name | (2R)-N-[(2S,3R,4E,8E)-1-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxy-9-methy l-4,8-octadecadien-2-yl]-2-hydroxyhexadecanamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1-O-Pivaloyl-glycerin
1-pivaloyloxypropane-2,3-diol Hexadecanamide, N-[(3E,7E)-1-[(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)methyl]-2-hydroxy-8-methyl-3,7-heptadecadien-1-yl]-2-hydroxy- Hexadecanamide, N-[(1S,2R,3E,7E)-1-[(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)methyl]-2-hydroxy-8-methyl-3,7-heptadecadien-1-yl]-2-hydroxy-, (2R)- N-[(4E,8E)-1-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxy-9-methyl-4,8-octadecadien-2-yl]-2-hydroxyhexadecanamide cerebroside (2R)-N-[(2S,3R,4E,8E)-1-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxy-9-methyl-4,8-octadecadien-2-yl]-2-hydroxyhexadecanamide Propanoic acid,2,2-dimethyl-,2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester glucocerebroside |
| Description | Cerebroside B, a sphingolipid compound, is a non-racespecific elicitor, which elicits defense responses in rice[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Treatment of lettuce (Lactuca sativa), tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum), melon (Cucumis melo), and sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) with Cerebroside B resulted in resistance to infection by each pathogenic strain of F. oxysporum. Induction of pathogenesis-related genes and H2O2 production by treatment with Cerebroside B are observed in tomato root tissues[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 876.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C41H77NO9 |
| Molecular Weight | 728.051 |
| Flash Point | 483.9±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 727.559814 |
| PSA | 168.94000 |
| LogP | 10.62 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |

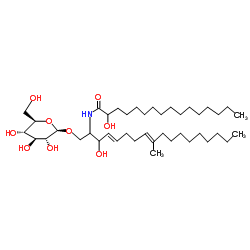
![1-O-(2'',3'',4'',6''-tetra-O-benzoyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-(2S,3R,4E,8E)-2-[(2'R)-2'-((benzoyloxy)hexadecanoyl)amino]-3-O-benzoyl-9-methyl-4,8-octadecadiene-1,3-diol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/447/1220969-59-4.png)