Bergamotine
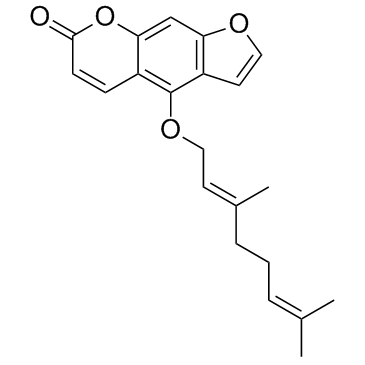
Bergamotine structure
|
Common Name | Bergamotine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7380-40-7 | Molecular Weight | 338.397 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 503.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O4 | Melting Point | 75-80ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 258.4±30.1 °C | |
Use of BergamotineBergamottin is a potent and competitive CYP1A1 inhibitor with a Ki of 10.703 nM. |
| Name | 4-[(2E)-3,7-dimethylocta-2,6-dienoxy]furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bergamottin is a potent and competitive CYP1A1 inhibitor with a Ki of 10.703 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CYP1A1:10.703 nM (Ki) CYP1A1:0.192 μM (IC50) CYP1A2:5.077 μM (IC50) CYP2B2:4.535 μM (IC50) CYP2B1:9.495 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Bergamottin is a competitive inhibitor of CYP1A1. Bergamottin inhibits CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2B1, and CYP2B2 with IC50s of 0.192±0.029 μM, 5.077±0.31 μM, 9.495±0.979 μM, 4.535±0.092 μM, respectively[1]. Bergamottin has potent antiproliferative effects on the A549 cells. Bergamottin shows both concentration-dependent as well as time‑dependent growth inhibitory effects against these cells. Bergamottin also inhibits the clonogenic activity of the A549 cancer cells by reducing the number of cancer colony forming cells. A reduction in clonogenicity also follows the concentration dependence on Bergamottin[2]. |
| In Vivo | The anticancer efficacy of Bergamottin under in vivo conditions using female BALB/c nude mice (a total of 20 mice are used) is determined. Tumors are induced in the mice by injecting non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells (1×106 cells/mouse). After tumor formation, the mice are sacrificed and tumors are removed and their weights and volumes are calculated. The results show that 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg Bergamottin injection reduce the tumor weight from 1.61 g in the PBS-treated group (control) to 1.21, 0.42 and 0.15 g, respectively. Tumor weight in the nude mice is reduced much more significantly in the highest-concentration Bergamottin group (100 mg/kg body weight) compared with the vehicle group (P<0.05). Likewise, 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg Bergamottin injection reduces the tumor volume from 2.2 cm3 in the PBS-treated group (control) to 1.71, 1.1 and 0.51 cm3, respectively. The periodic measurement of the tumor xenograft volume indicates that the tumor volume in the nude mice is reduced considerably in the highest-concentration Bergamottin group (100 mg/kg body weight) compared with the vehicle group (P<0.05)[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | CYP1A1 Supersomes and different concentrations of 7-ethoxyresorufin (ER) are used to determine CYP1A1 enzymatic kinetics. A typical Michaelis-Menten curve is found. The final reaction mixture contains: 1 pmol CYP1A1, 0.5 mM NADPH, different ER concentrations and 0, 4, 8 and 16 nM of Bergamottin (BG). The reaction is started with the addition of NADPH. Kinetic constants are obtained by a nonlinear regression analysis of experimental data fitted to Michaelis-Menten equation with competitive-type inhibition. Kinetic analysis is also shown by using the Lineweaver-Burk, Dixon and replot of the slopes of the Dixon plot[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Inhibition of cell proliferation by Bergamottin is measured by the MTT assay. Briefly, the human lung adenocarcinoma cancer A549 cells are plated in 96-well culture plates (1×105 cells/well). After 24 h of incubation, the cells are treated with Bergamottin (0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75 and 100 μM) for 24 and 48 h, MTT solution (10 mg/mL) is then added to each well. After a 4-h incubation, the formazan precipitate is dissolved in 100 μL DMSO, and then the absorbance is measured in an automated microplated reader at 570 nm. The cell viability ratio is calculated. Cytotoxicity is expressed as the concentration of Bergamottin needed to inhibit cell growth by 50% (IC50 value)[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Female BALB/c nude mice (six weeks old) (a total of 20 are obtained) are maintained with water and food ad libitum in a pathogen-free environment with a 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle in an animal care facility. Human non‑small cell lung carcinoma A549 cells (2×106 cells/mouse) are injected into the right axilla of the nude mice (5 mice/group) to create tumors in the mice. Subsequent to tumor development, the mice are divided into 4 groups and treated with Bergamottin injected intraperitoneally. The control group in the study is treated with an equal amount of PBS while the other three groups are treated with 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg of Bergamottin. Afterwards, the mice are sacrificed after 18 days, and the tumor weight and volume of each mouse are evaluated. Tumor length and width are measured using a Vernier caliper and the tumor volume (TV) is calculated[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 503.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 75-80ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 338.397 |
| Flash Point | 258.4±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 338.151794 |
| PSA | 52.58000 |
| LogP | 5.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.583 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Grapefruit (Citrus paradisi Macfad) phytochemicals composition is modulated by household processing techniques.
J. Food Sci. 77(9) , C921-6, (2012) Grapefruits (Citrus paradisi Macfad) contain several phytochemicals known to have health maintaining properties. Due to the consumer's interest in obtaining high levels of these phytochemicals, it is ... |
|
|
Structure-activity relationships for naturally occurring coumarins as β-secretase inhibitor.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20 , 784-8, (2012) The present study was demonstrated to evaluate the effects of naturally occurring coumarins (NOCs) including simple coumarins, furanocoumarins, and pyranocoumarins on the inhibition of β-secretase (BA... |
|
|
Chemical composition of hexane extract of Citrus aurantifolia and anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity of some of its constituents.
Molecules 17(9) , 11173-84, (2012) The main aim of this study was to isolate and characterize the active compounds from the hexane extract of the fruit peels of Citrus aurantiifolia, which showed activity against one sensitive and thre... |
| 4-([(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl]oxy)-7h-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one |
| 4-{[(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl]oxy}-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one |
| Bergamottin |
| Bergaptin |
| 5-geranyloxypsoralen |
| Bergamotine |
| 4-{[(2'E)-3',7'-dimethyl-2',6'-octadienyl]oxy}-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one |
| 4-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-yl]oxy}-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one |
| 4-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy}-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one |
| 5-Geranoxypsoralen |
| Bergomottin |
| 5-geranyloxypsolaren |
| 7H-Furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one, 4-[[(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy]- |
| 7H-Furo(3,2-g)(1)benzopyran-7-one, 4-((3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)oxy)-, (E)- |
| Bergamotin |
 CAS#:6138-90-5
CAS#:6138-90-5 CAS#:486-60-2
CAS#:486-60-2 CAS#:484-20-8
CAS#:484-20-8 CAS#:145414-76-2
CAS#:145414-76-2
