Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methane
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 17:35:10
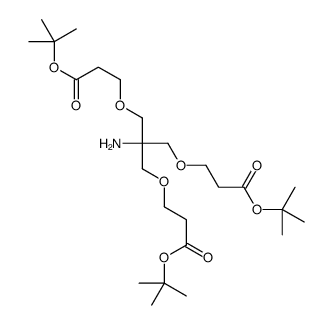
Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methane structure
|
Common Name | Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 175724-30-8 | Molecular Weight | 505.64200 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H47NO9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methaneTris[[2-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)ethoxy]methyl]methylamine is a cleavable PEG ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methane is also a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
| Name | Tris[[2-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)ethoxy]methyl]methylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tris[[2-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)ethoxy]methyl]methylamine is a cleavable PEG ADC linker used in the synthesis of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Amino-Tri-(t-butoxycarbonylethoxymethyl)-methane is also a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used in the synthesis of PROTACs[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PEGs Cleavable |
| In Vitro | ADCs are comprised of an antibody to which is attached an ADC cytotoxin through an ADC linker[1]. PROTACs contain two different ligands connected by a linker; one is a ligand for an E3 ubiquitin ligase and the other is for the target protein. PROTACs exploit the intracellular ubiquitin-proteasome system to selectively degrade target proteins[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H47NO9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 505.64200 |
| Exact Mass | 505.32500 |
| PSA | 132.61000 |
| LogP | 3.62940 |
| tert-butyl 3-[2-amino-3-[3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxopropoxy]-2-[[3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxopropoxy]methyl]propoxy]propanoate |