Luteolin
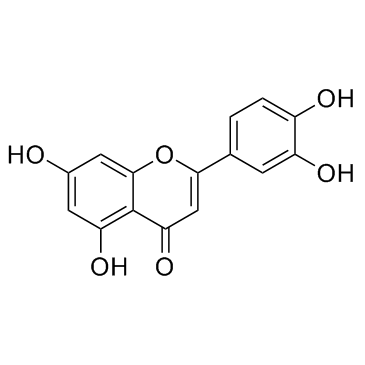
Luteolin structure
|
Common Name | Luteolin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 491-70-3 | Molecular Weight | 286.236 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 616.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O6 | Melting Point | ~330 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 239.5±25.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of LuteolinLuteolin is a falconoid compound, which exhibits anticancer properties.IC50 value:Target: A natural for anticancer.In vitro: Luteolin exerted an anticancer effect against NCI-H460 cells through Sirt1-mediated apoptosis and the inhibition of cell migration [1]. The treatment of luteolin upregulated the expression levels of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), p21WAF1/CIP1, p27KIP1, Smad4, and Fas in HCC cells. Luteolin induced apoptotic cell death in Hep3B cells while caused G1 arrest in HepG2 cells. And it induces apoptosis from G1 arrest via three signaling pathways of TGF-β1, p53, and Fas/Fas-ligand in HCC cells [2].In vivo: The study of the effect of Luteolin on the improvement of cancerous cachexia in model mice showed that luteolin can improve the symptoms of cancer cachexia model mice.The mechanism may be related to inhibition of proteasome and calcium activated protease activity and lower the levels of cytokines [3]. |
| Name | luteolin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Luteolin is a falconoid compound, which exhibits anticancer properties.IC50 value:Target: A natural for anticancer.In vitro: Luteolin exerted an anticancer effect against NCI-H460 cells through Sirt1-mediated apoptosis and the inhibition of cell migration [1]. The treatment of luteolin upregulated the expression levels of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), p21WAF1/CIP1, p27KIP1, Smad4, and Fas in HCC cells. Luteolin induced apoptotic cell death in Hep3B cells while caused G1 arrest in HepG2 cells. And it induces apoptosis from G1 arrest via three signaling pathways of TGF-β1, p53, and Fas/Fas-ligand in HCC cells [2].In vivo: The study of the effect of Luteolin on the improvement of cancerous cachexia in model mice showed that luteolin can improve the symptoms of cancer cachexia model mice.The mechanism may be related to inhibition of proteasome and calcium activated protease activity and lower the levels of cytokines [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 616.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | ~330 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 286.236 |
| Flash Point | 239.5±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 286.047729 |
| PSA | 111.13000 |
| LogP | 2.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.768 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | LK9275210 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2914501900 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914501900 other ketone-phenols。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
A Food-Derived Flavonoid Luteolin Protects against Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Remodeling.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0137106, (2015) Oxidative stress has been implicated in cardiac remodeling (cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy), which impairs cardiac function and metabolism; therefore, it is anticipated antioxidative compounds will ... |
|
|
Sesquiterpenes with TRAIL-resistance overcoming activity from Xanthium strumarium.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 , 4746-54, (2015) The ability of TRAIL to selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing normal cells makes it an attractive target for the development of new cancer therapy. In search of bioactive natural ... |
|
|
Metabolite profiling of polyphenols in the Tunisian plant Tamarix aphylla (L.) Karst.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 99 , 97-105, (2014) In this study, a detailed investigation on the composition of polyphenols of Tamarix aphylla (L.) Karst., consisting of phenolic acids and flavonoids, was carried out. In order to optimize the yield o... |
| EINECS 207-741-0 |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy- |
| Flavopurpol |
| 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavon |
| 3' 4' 5 7-tetrahydroxyflavone |
| LUTEOLOL |
| 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxy-flavone |
| FLACITRAN |
| Cyanidenon 1470 |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one |
| Digitoflavone |
| 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-benzopyrone |
| 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavone |
| Daphneflavonol |
| weldlake |
| cyanidenon |
| Luteolin |
| 3',4',5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone |
| Salifazide |
| MFCD08460272 |
 CAS#:855-97-0
CAS#:855-97-0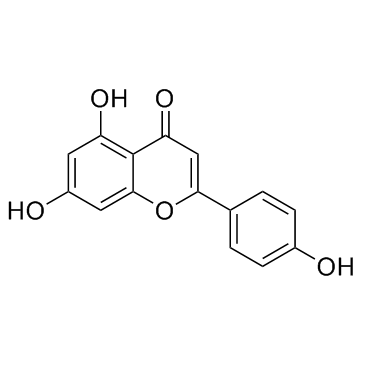 CAS#:520-36-5
CAS#:520-36-5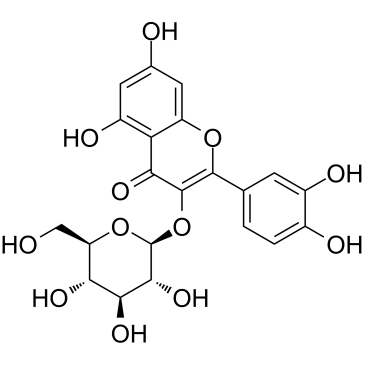 CAS#:482-35-9
CAS#:482-35-9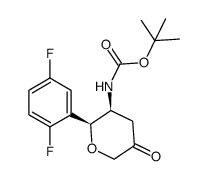 CAS#:58124-13-3
CAS#:58124-13-3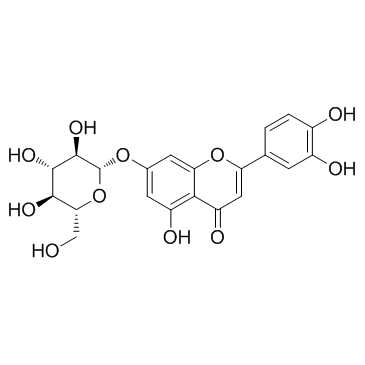 CAS#:5373-11-5
CAS#:5373-11-5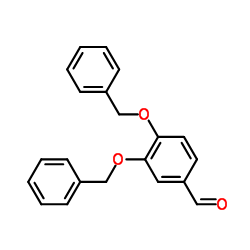 CAS#:5447-02-9
CAS#:5447-02-9![1-[2-hydroxy-4,6-bis(methoxymethoxy)phenyl]ethanone Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/448/65490-09-7.png) CAS#:65490-09-7
CAS#:65490-09-7![[2-acetyloxy-4-(5,7-diacetyloxy-4-oxochromen-2-yl)phenyl] acetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/096/1061-93-4.png) CAS#:1061-93-4
CAS#:1061-93-4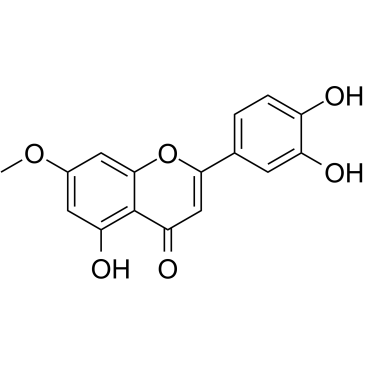 CAS#:20243-59-8
CAS#:20243-59-8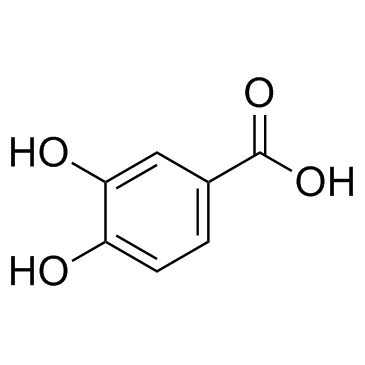 CAS#:99-50-3
CAS#:99-50-3 CAS#:108-73-6
CAS#:108-73-6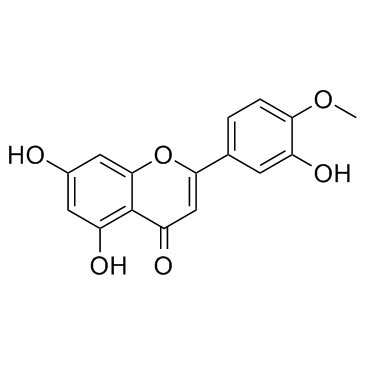 CAS#:520-34-3
CAS#:520-34-3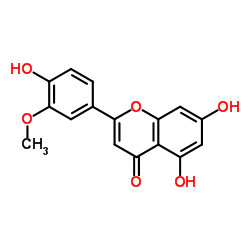 CAS#:491-71-4
CAS#:491-71-4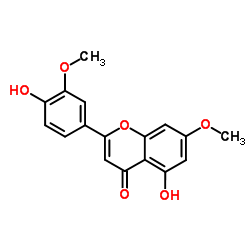 CAS#:25739-41-7
CAS#:25739-41-7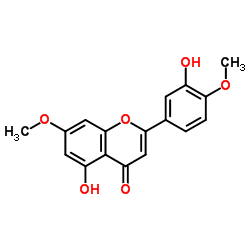 CAS#:32174-62-2
CAS#:32174-62-2 CAS#:29080-58-8
CAS#:29080-58-8
